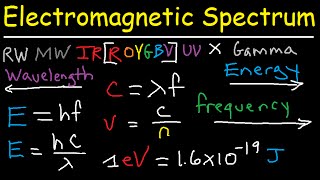32. Electromagnetic Waves
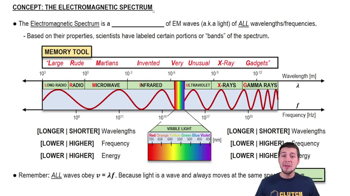
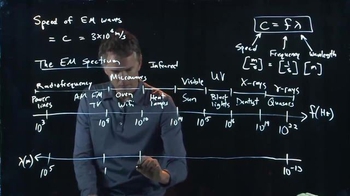
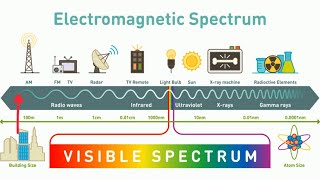
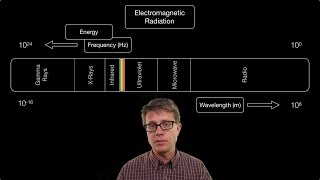
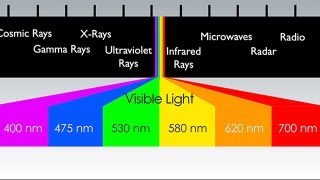
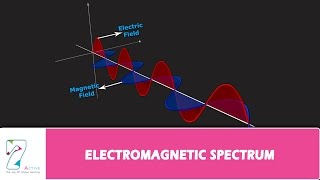
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following types of electromagnetic waves has the longest wavelength?1110views
- Multiple Choice
A standard cell phone transmitselectromagnetic waves with afrequency of .Calculatethewavelengthof these electromagnetic waves (in cm).
1295views14rank1comments - Textbook Question
(I) What is the range of wavelengths for (a) FM radio (88 MHz to 108 MHz) and (b) AM radio (535 kHz to 1700 kHz)?
1134views - Textbook Question
(I) An EM wave has frequency 2.65 x 1014 Hz. What is its wavelength, and how would we classify it?
1058views - Textbook Question
(III) Stars located in a certain cluster are assumed to be about the same distance from us. Two such stars have spectra that peak at λ1 = 470nm and λ2 = 720 nm, and the ratio of their apparent brightness is b1/b2 = 0.091. Estimate their relative sizes (give ratio of their diameters) using Wien’s law and the Stefan-Boltzmann equation, Eq. 19–17.
608views - Textbook Question
In free space (“vacuum”), where the net charge and current flow is zero, the speed of an EM wave is given by v = 1 √(ε₀μ₀). If, instead, an EM wave travels in a nonconducting (“dielectric”) material with dielectric constant K, then v = 1 √(Kε₀μ₀). For frequencies corresponding to the visible spectrum (near 5 x 1014 Hz), the dielectric constant of water is 1.77. Predict the speed of light in water and compare this value (as a percentage) with the speed of light in a vacuum.
746views