15. Rotational Equilibrium
Equilibrium in 2D - Ladder Problems
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
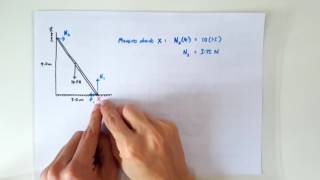
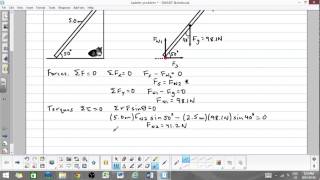
A ladder of mass 20 kg (uniformly distributed) and length 6 m rests against a vertical wall while making an angle of Θ = 60° with the horizontal, as shown. A 50 kg girl climbs 2 m up the ladder. Calculate the magnitude of the total contact force at the bottom of the ladder (Remember:You will need to first calculate the magnitude of N,BOT and f,S).
1229views5rank7comments - Textbook Question
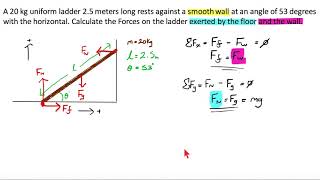
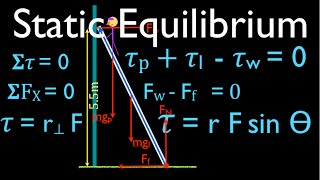
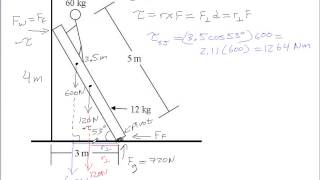
A uniform ladder 5.0 m long rests against a frictionless, vertical wall with its lower end 3.0 m from the wall. The ladder weighs 160 N. The coefficient of static friction between the foot of the ladder and the ground is 0.40. A man weighing 740 N climbs slowly up the ladder. Start by drawing a free-body diagram of the ladder. What is the maximum friction force that the ground can exert on the ladder at its lower end?
2416views - Textbook Question
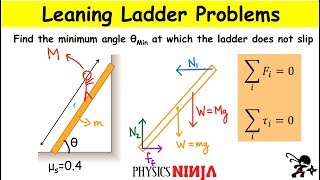
A 3.0-m-long ladder, as shown in Figure 12.35, leans against a frictionless wall. The coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the floor is 0.40. What is the minimum angle the ladder can make with the floor without slipping?
1646views - Textbook Question
(III) Consider a ladder with a painter climbing up it (Fig. 12–71). The mass of the uniform ladder is 12.0 kg, and the mass of the painter is 55.0 kg. If the ladder begins to slip at its base when the painter’s feet are 70% of the way up the length of the ladder, what is the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the floor? Assume the wall is frictionless.
<IMAGE>
1092views - Textbook Question
Two identical, uniform beams are symmetrically set up against each other (Fig. 12–95) on a floor with which they have a coefficient of friction μs = 0.45. What is the minimum angle the beams can make with the floor and still not fall?
617views