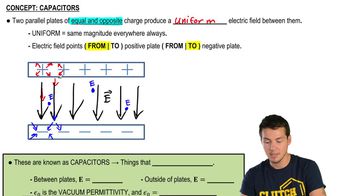
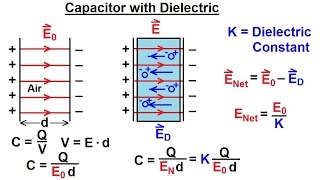
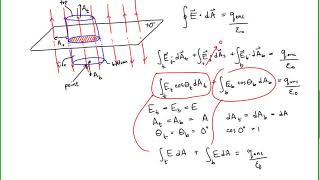
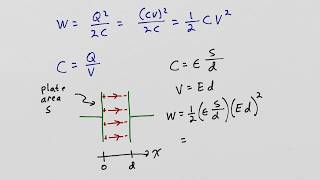24. Electric Force & Field; Gauss' Law
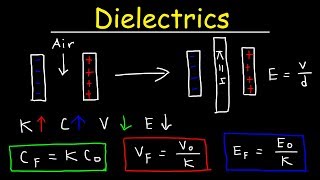
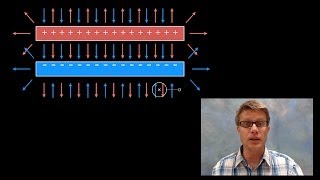
Electric Fields in Capacitors
24. Electric Force & Field; Gauss' Law
Electric Fields in Capacitors
Additional 4 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 7 of 7 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
An electron moves into a capacitor at an initial speed of 150 m/s. If the electron enters exactly halfway between the plates, how far will the electron move horizontally before it strikes one of the plates? Which plate will it strike?
1445views32rank9comments - Multiple ChoiceEach plate in a parallel-plate capacitor has an area of . and the separation between plates is . The magnitude of the charge on each plate is . What is the magnitude of the electric field between the plates and inside the metal of the plates?459views
- Multiple ChoiceA water molecule is a dipole. If water were placed in the uniform field between capacitor plates, which of the following would best describe the force and torque experienced by the water molecules?845views
- Textbook QuestionINT FIGURE EX23.25 shows a 1.5 g ball hanging from a string inside a parallel-plate capacitor made with 12 cm×12 cm electrodes. The electrodes are charged to ±75 nC . What is the charge on the ball in nC?1019views1rank
- Textbook QuestionINT Electrostatic cleaners remove small dust particles and pollen grains from air by first ionizing them, then flowing the air between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor, parallel to the plates, where electric forces deposit charged particles on one of the electrodes. A typical pollen grain has a mass of 5.0×10^−10 g, the ionizer charges it with 750 extra electrons, and a fan moves the air at 3.0 m/s. Ignore air resistance and gravity. b. What minimum electric field strength is needed to deflect the grain by 3.0 mm before it leaves the electrodes?603views
- Textbook QuestionOne type of ink-jet printer, called an electrostatic ink-jet printer, forms the letters by using deflecting electrodes to steer charged ink drops up and down vertically as the ink jet sweeps horizontally across the page. The ink jet forms 30-μm-diameter drops of ink, charges them by spraying 800,000 electrons on the surface, and shoots them toward the page at a speed of 20 m/s . Along the way, the drops pass through two horizontal, parallel electrodes that are 6.0 mm long, 4.0 mm wide, and spaced 1.0 mm apart. The distance from the center of the electrodes to the paper is 2.0 cm. To form the tallest letters, which have a height of 6.0 mm, the drops need to be deflected upward (or downward) by 3.0 mm. What electric field strength is needed between the electrodes to achieve this deflection? Ink, which consists of dye particles suspended in alcohol, has a density of 800 kg/m^3 .412views
- Textbook QuestionCP A proton is traveling horizontally to the right at 4.50 * 10^6 m/s. (a) Find the magnitude and direction of the weakest electric field that can bring the proton uniformly to rest over a distance of 3.20 cm.2010views7rank