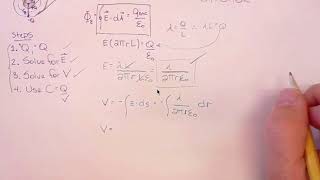26. Capacitors & Dielectrics
Capacitance Using Calculus
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
In the figure, . The switch has been in position a for a long time. At the switch is moved to position b. At what time will the voltmeter read828views - Textbook Question
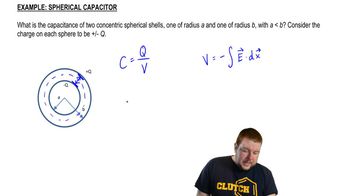
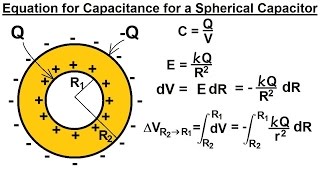
Find an expression for the capacitance of a spherical capacitor, consisting of concentric spherical shells of radii R1 (inner shell) and R2 (outer shell).
78views - Textbook Question
High-frequency signals are often transmitted along a coaxial cable, such as the one shown in FIGURE P26.68. For example, the cable TV hookup coming into your home is a coaxial cable. The signal is carried on a wire of radius R1 while the outer conductor of radius R2 is grounded (i.e., at V=0 V). An insulating material fills the space between them, and an insulating plastic coating goes around the outside. Evaluate the capacitance per meter of a cable having R1=0.50 mm and R2=3.0 mm.
73views - Textbook Question
A spherical capacitor contains a charge of nC when connected to a potential difference of V. If its plates are separated by vacuum and the inner radius of the outer shell is cm, calculate: (a) the capacitance; (b) the radius of the inner sphere; (c) the electric field just outside the surface of the inner sphere.
1793views - Textbook Question
A capacitor is made from two hollow, coaxial, iron cylinders, one inside the other. The inner cylinder is negatively charged and the outer is positively charged; the magnitude of the charge on each is pC. The inner cylinder has radius mm, the outer one has radius mm, and the length of each cylinder is cm.
(a) What is the capacitance?
(b) What applied potential difference is necessary to produce these charges on the cylinders?
1271views