In this page, we're going to discuss another product that forms when carbonyls react with alcohols, and that's called acetals. In general, I'm just going to say a few facts, and then we're going to go straight into the mechanism. The first fact I want you to know is that acetals, once formed, are actually stable in base. If you want to keep an acetal for a long time, keep it in a neutral to basic solution. However, they're easily hydrolyzed back to carbonyls using acid. That makes sense, guys, because remember that this is a reversible reaction. It's acid catalyzed. It makes sense that if you use acid, you're going to go back to the carbonyl and it's going to be in equilibrium. If you want to specifically make an acetal that not only has ROR but is actually cyclic, meaning it forms a ring, then you're going to have to use a diol because a diol is going to have carbons in the middle that are going to link together. For example, the diol that I would need here would be 1,2-ethanediol
- 1. A Review of General Chemistry5h 5m
- Summary23m
- Intro to Organic Chemistry5m
- Atomic Structure16m
- Wave Function9m
- Molecular Orbitals17m
- Sigma and Pi Bonds9m
- Octet Rule12m
- Bonding Preferences12m
- Formal Charges6m
- Skeletal Structure14m
- Lewis Structure20m
- Condensed Structural Formula15m
- Degrees of Unsaturation15m
- Constitutional Isomers14m
- Resonance Structures46m
- Hybridization23m
- Molecular Geometry16m
- Electronegativity22m
- 2. Molecular Representations1h 14m
- 3. Acids and Bases2h 46m
- 4. Alkanes and Cycloalkanes4h 19m
- IUPAC Naming29m
- Alkyl Groups13m
- Naming Cycloalkanes10m
- Naming Bicyclic Compounds10m
- Naming Alkyl Halides7m
- Naming Alkenes3m
- Naming Alcohols8m
- Naming Amines15m
- Cis vs Trans21m
- Conformational Isomers13m
- Newman Projections14m
- Drawing Newman Projections16m
- Barrier To Rotation7m
- Ring Strain8m
- Axial vs Equatorial7m
- Cis vs Trans Conformations4m
- Equatorial Preference14m
- Chair Flip9m
- Calculating Energy Difference Between Chair Conformations17m
- A-Values17m
- Decalin7m
- 5. Chirality3h 39m
- Constitutional Isomers vs. Stereoisomers9m
- Chirality12m
- Test 1:Plane of Symmetry7m
- Test 2:Stereocenter Test17m
- R and S Configuration43m
- Enantiomers vs. Diastereomers13m
- Atropisomers9m
- Meso Compound12m
- Test 3:Disubstituted Cycloalkanes13m
- What is the Relationship Between Isomers?16m
- Fischer Projection10m
- R and S of Fischer Projections7m
- Optical Activity5m
- Enantiomeric Excess20m
- Calculations with Enantiomeric Percentages11m
- Non-Carbon Chiral Centers8m
- 6. Thermodynamics and Kinetics1h 22m
- 7. Substitution Reactions1h 48m
- 8. Elimination Reactions2h 30m
- 9. Alkenes and Alkynes2h 9m
- 10. Addition Reactions3h 18m
- Addition Reaction6m
- Markovnikov5m
- Hydrohalogenation6m
- Acid-Catalyzed Hydration17m
- Oxymercuration15m
- Hydroboration26m
- Hydrogenation6m
- Halogenation6m
- Halohydrin12m
- Carbene12m
- Epoxidation8m
- Epoxide Reactions9m
- Dihydroxylation8m
- Ozonolysis7m
- Ozonolysis Full Mechanism24m
- Oxidative Cleavage3m
- Alkyne Oxidative Cleavage6m
- Alkyne Hydrohalogenation3m
- Alkyne Halogenation2m
- Alkyne Hydration6m
- Alkyne Hydroboration2m
- 11. Radical Reactions1h 58m
- 12. Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides and Thiols2h 42m
- Alcohol Nomenclature4m
- Naming Ethers6m
- Naming Epoxides18m
- Naming Thiols11m
- Alcohol Synthesis7m
- Leaving Group Conversions - Using HX11m
- Leaving Group Conversions - SOCl2 and PBr313m
- Leaving Group Conversions - Sulfonyl Chlorides7m
- Leaving Group Conversions Summary4m
- Williamson Ether Synthesis3m
- Making Ethers - Alkoxymercuration4m
- Making Ethers - Alcohol Condensation4m
- Making Ethers - Acid-Catalyzed Alkoxylation4m
- Making Ethers - Cumulative Practice10m
- Ether Cleavage8m
- Alcohol Protecting Groups3m
- t-Butyl Ether Protecting Groups5m
- Silyl Ether Protecting Groups10m
- Sharpless Epoxidation9m
- Thiol Reactions6m
- Sulfide Oxidation4m
- 13. Alcohols and Carbonyl Compounds2h 17m
- 14. Synthetic Techniques1h 26m
- 15. Analytical Techniques:IR, NMR, Mass Spect7h 3m
- Purpose of Analytical Techniques5m
- Infrared Spectroscopy16m
- Infrared Spectroscopy Table31m
- IR Spect:Drawing Spectra40m
- IR Spect:Extra Practice26m
- NMR Spectroscopy10m
- 1H NMR:Number of Signals26m
- 1H NMR:Q-Test26m
- 1H NMR:E/Z Diastereoisomerism8m
- H NMR Table24m
- 1H NMR:Spin-Splitting (N + 1) Rule22m
- 1H NMR:Spin-Splitting Simple Tree Diagrams11m
- 1H NMR:Spin-Splitting Complex Tree Diagrams12m
- 1H NMR:Spin-Splitting Patterns8m
- NMR Integration18m
- NMR Practice14m
- Carbon NMR4m
- Structure Determination without Mass Spect47m
- Mass Spectrometry12m
- Mass Spect:Fragmentation28m
- Mass Spect:Isotopes27m
- 16. Conjugated Systems6h 13m
- Conjugation Chemistry13m
- Stability of Conjugated Intermediates4m
- Allylic Halogenation12m
- Reactions at the Allylic Position39m
- Conjugated Hydrohalogenation (1,2 vs 1,4 addition)26m
- Diels-Alder Reaction9m
- Diels-Alder Forming Bridged Products11m
- Diels-Alder Retrosynthesis8m
- Molecular Orbital Theory9m
- Drawing Atomic Orbitals6m
- Drawing Molecular Orbitals17m
- HOMO LUMO4m
- Orbital Diagram:3-atoms- Allylic Ions13m
- Orbital Diagram:4-atoms- 1,3-butadiene11m
- Orbital Diagram:5-atoms- Allylic Ions10m
- Orbital Diagram:6-atoms- 1,3,5-hexatriene13m
- Orbital Diagram:Excited States4m
- Pericyclic Reaction10m
- Thermal Cycloaddition Reactions26m
- Photochemical Cycloaddition Reactions26m
- Thermal Electrocyclic Reactions14m
- Photochemical Electrocyclic Reactions10m
- Cumulative Electrocyclic Problems25m
- Sigmatropic Rearrangement17m
- Cope Rearrangement9m
- Claisen Rearrangement15m
- 17. Ultraviolet Spectroscopy51m
- 18. Aromaticity2h 34m
- 19. Reactions of Aromatics: EAS and Beyond5h 1m
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution9m
- Benzene Reactions11m
- EAS:Halogenation Mechanism6m
- EAS:Nitration Mechanism9m
- EAS:Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Mechanism6m
- EAS:Friedel-Crafts Acylation Mechanism5m
- EAS:Any Carbocation Mechanism7m
- Electron Withdrawing Groups22m
- EAS:Ortho vs. Para Positions4m
- Acylation of Aniline9m
- Limitations of Friedel-Crafts Alkyation19m
- Advantages of Friedel-Crafts Acylation6m
- Blocking Groups - Sulfonic Acid12m
- EAS:Synergistic and Competitive Groups13m
- Side-Chain Halogenation6m
- Side-Chain Oxidation4m
- Reactions at Benzylic Positions31m
- Birch Reduction10m
- EAS:Sequence Groups4m
- EAS:Retrosynthesis29m
- Diazo Replacement Reactions6m
- Diazo Sequence Groups5m
- Diazo Retrosynthesis13m
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution28m
- Benzyne16m
- 20. Phenols55m
- 21. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition4h 56m
- Naming Aldehydes8m
- Naming Ketones7m
- Oxidizing and Reducing Agents9m
- Oxidation of Alcohols28m
- Ozonolysis7m
- DIBAL5m
- Alkyne Hydration9m
- Nucleophilic Addition8m
- Cyanohydrin11m
- Organometallics on Ketones19m
- Overview of Nucleophilic Addition of Solvents13m
- Hydrates6m
- Hemiacetal9m
- Acetal12m
- Acetal Protecting Group16m
- Thioacetal6m
- Imine vs Enamine15m
- Addition of Amine Derivatives5m
- Wolff Kishner Reduction7m
- Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation39m
- Acid Chloride to Ketone7m
- Nitrile to Ketone9m
- Wittig Reaction18m
- Ketone and Aldehyde Synthesis Reactions14m
- 22. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: NAS2h 51m
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives7m
- Naming Carboxylic Acids9m
- Diacid Nomenclature6m
- Naming Esters5m
- Naming Nitriles3m
- Acid Chloride Nomenclature5m
- Naming Anhydrides7m
- Naming Amides5m
- Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution18m
- Carboxylic Acid to Acid Chloride6m
- Fischer Esterification5m
- Acid-Catalyzed Ester Hydrolysis4m
- Saponification3m
- Transesterification5m
- Lactones, Lactams and Cyclization Reactions10m
- Carboxylation5m
- Decarboxylation Mechanism14m
- Review of Nitriles46m
- 23. The Chemistry of Thioesters, Phophate Ester and Phosphate Anhydrides1h 10m
- 24. Enolate Chemistry: Reactions at the Alpha-Carbon1h 53m
- Tautomerization9m
- Tautomers of Dicarbonyl Compounds6m
- Enolate4m
- Acid-Catalyzed Alpha-Halogentation4m
- Base-Catalyzed Alpha-Halogentation3m
- Haloform Reaction8m
- Hell-Volhard-Zelinski Reaction3m
- Overview of Alpha-Alkylations and Acylations5m
- Enolate Alkylation and Acylation12m
- Enamine Alkylation and Acylation16m
- Beta-Dicarbonyl Synthesis Pathway7m
- Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis13m
- Malonic Ester Synthesis15m
- 25. Condensation Chemistry2h 9m
- 26. Amines1h 43m
- 27. Heterocycles2h 0m
- Nomenclature of Heterocycles15m
- Acid-Base Properties of Nitrogen Heterocycles10m
- Reactions of Pyrrole, Furan, and Thiophene13m
- Directing Effects in Substituted Pyrroles, Furans, and Thiophenes16m
- Addition Reactions of Furan8m
- EAS Reactions of Pyridine17m
- SNAr Reactions of Pyridine18m
- Side-Chain Reactions of Substituted Pyridines20m
- 28. Carbohydrates5h 53m
- Monosaccharide20m
- Monosaccharides - D and L Isomerism9m
- Monosaccharides - Drawing Fischer Projections18m
- Monosaccharides - Common Structures6m
- Monosaccharides - Forming Cyclic Hemiacetals12m
- Monosaccharides - Cyclization18m
- Monosaccharides - Haworth Projections13m
- Mutarotation11m
- Epimerization9m
- Monosaccharides - Aldose-Ketose Rearrangement8m
- Monosaccharides - Alkylation10m
- Monosaccharides - Acylation7m
- Glycoside6m
- Monosaccharides - N-Glycosides18m
- Monosaccharides - Reduction (Alditols)12m
- Monosaccharides - Weak Oxidation (Aldonic Acid)7m
- Reducing Sugars23m
- Monosaccharides - Strong Oxidation (Aldaric Acid)11m
- Monosaccharides - Oxidative Cleavage27m
- Monosaccharides - Osazones10m
- Monosaccharides - Kiliani-Fischer23m
- Monosaccharides - Wohl Degradation12m
- Monosaccharides - Ruff Degradation12m
- Disaccharide30m
- Polysaccharide11m
- 29. Amino Acids3h 20m
- Proteins and Amino Acids19m
- L and D Amino Acids14m
- Polar Amino Acids14m
- Amino Acid Chart18m
- Acid-Base Properties of Amino Acids33m
- Isoelectric Point14m
- Amino Acid Synthesis: HVZ Method12m
- Synthesis of Amino Acids: Acetamidomalonic Ester Synthesis16m
- Synthesis of Amino Acids: N-Phthalimidomalonic Ester Synthesis13m
- Synthesis of Amino Acids: Strecker Synthesis13m
- Reactions of Amino Acids: Esterification7m
- Reactions of Amino Acids: Acylation3m
- Reactions of Amino Acids: Hydrogenolysis6m
- Reactions of Amino Acids: Ninhydrin Test11m
- 30. Peptides and Proteins2h 42m
- Peptides12m
- Primary Protein Structure4m
- Secondary Protein Structure17m
- Tertiary Protein Structure11m
- Disulfide Bonds17m
- Quaternary Protein Structure10m
- Summary of Protein Structure7m
- Intro to Peptide Sequencing2m
- Peptide Sequencing: Partial Hydrolysis25m
- Peptide Sequencing: Partial Hydrolysis with Cyanogen Bromide7m
- Peptide Sequencing: Edman Degradation28m
- Merrifield Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis18m
- 32. Lipids 2h 50m
- 34. Nucleic Acids1h 32m
- 35. Transition Metals5h 33m
- Electron Configuration of Elements45m
- Coordination Complexes20m
- Ligands24m
- Electron Counting10m
- The 18 and 16 Electron Rule13m
- Cross-Coupling General Reactions40m
- Heck Reaction40m
- Stille Reaction13m
- Suzuki Reaction25m
- Sonogashira Coupling Reaction17m
- Fukuyama Coupling Reaction15m
- Kumada Coupling Reaction13m
- Negishi Coupling Reaction16m
- Buchwald-Hartwig Amination Reaction19m
- Eglinton Reaction17m
Acetal - Online Tutor, Practice Problems & Exam Prep
 Created using AI
Created using AIAcetals form when carbonyls react with alcohols, remaining stable in basic conditions but easily hydrolyzed back to carbonyls in acidic environments. The mechanism involves an acid-catalyzed process, starting with protonation, followed by nucleophilic addition, and concluding with deprotonation. To create cyclic acetals, diols are necessary. Understanding this mechanism is crucial, as it is frequently tested in organic chemistry, emphasizing the importance of recognizing the roles of hemiacetals and the choice of protonation to drive the reaction forward.
General Mechanism
Video transcript
Provide the chemical steps necessary for the following synthesis.

Problem Transcript
Provide the chemical steps necessary for the following synthesis.
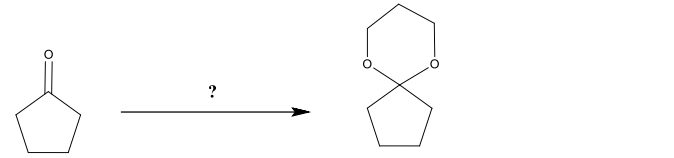
Problem Transcript
Determine the starting materials based on the acetal group present.

Problem Transcript
Do you want more practice?
More setsHere’s what students ask on this topic:
What is the mechanism for acetal formation?
The mechanism for acetal formation involves several steps, starting with the protonation of the carbonyl oxygen, making the carbonyl carbon more electrophilic. This is followed by nucleophilic addition of an alcohol to form a hemiacetal. The hemiacetal then undergoes protonation again, leading to the formation of a good leaving group (water), which departs to form a carbocation. Another molecule of alcohol then attacks the carbocation, followed by deprotonation to yield the final acetal. The overall process is acid-catalyzed and involves protonation, nucleophilic addition, formation of a leaving group, and deprotonation.
 Created using AI
Created using AIWhy are acetals stable in basic conditions but not in acidic conditions?
Acetals are stable in basic conditions because bases do not provide the necessary protons to initiate the reverse reaction back to carbonyls. In contrast, acidic conditions provide protons that can protonate the acetal, making it susceptible to hydrolysis. The protonation of the acetal oxygen creates a good leaving group (water), which facilitates the breakdown of the acetal back to the original carbonyl compound. This reversibility in acidic conditions is due to the equilibrium nature of the acetal formation reaction.
 Created using AI
Created using AIWhat is the difference between a hemiacetal and an acetal?
A hemiacetal contains one -OH group and one -OR group attached to the same carbon, whereas an acetal has two -OR groups attached to the same carbon. Hemiacetals are intermediates in the formation of acetals and can be formed under both acidic and basic conditions. However, to convert a hemiacetal to an acetal, an acid-catalyzed mechanism is required. The formation of an acetal involves the loss of water and the addition of a second alcohol molecule.
 Created using AI
Created using AIHow do you form a cyclic acetal?
To form a cyclic acetal, a diol (a molecule with two hydroxyl groups) is used. The diol reacts with a carbonyl compound in the presence of an acid catalyst. The first hydroxyl group of the diol forms a hemiacetal with the carbonyl, and then the second hydroxyl group reacts to form the acetal, resulting in a ring structure. For example, using 1,2-ethanediol with a carbonyl compound will form a five-membered cyclic acetal.
 Created using AI
Created using AIWhat role does protonation play in the formation of acetals?
Protonation plays a crucial role in the formation of acetals by increasing the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon, making it more susceptible to nucleophilic attack by an alcohol. The initial protonation of the carbonyl oxygen facilitates the formation of a hemiacetal. Subsequent protonation of the hemiacetal's hydroxyl group creates a good leaving group (water), which departs to form a carbocation. This carbocation is then attacked by another alcohol molecule, followed by deprotonation to yield the final acetal.
 Created using AI
Created using AIYour Organic Chemistry tutors
- (•) For each of the following reactions, identify the bonds that are broken and formed. Be sure to indicate wh...
- What are the products of the following reactions? e.
- Draw the products of the following reactions: b.
- Biochemists studying the structure of collagen (a fibrous protein in connective tissue) found cross-links con...
- Propose mechanisms for the following reactions.(a) <IMAGE of reaction>
- Draw structures of the following derivatives.(e) acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal
- Predict the products formed when cyclohexanone reacts with the following reagents.(b) excess CH3OH, H+
- Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with the following reagents.(d) excess ethanol...
- Alcohols combine with ketones and aldehydes to form interesting derivatives, which we will discuss in Chapter ...
- For each compound,1. name the functional group.2. show what compound(s) result from complete hydrolysis.(d) &l...
- For each compound,1. name the functional group.2. show what compound(s) result from complete hydrolysis.(e) &l...
- There are three dioxane isomers: 1,2-dioxane, 1,3-dioxane, and 1,4-dioxane. One of these acts like an ether an...
- There are three dioxane isomers: 1,2-dioxane, 1,3-dioxane, and 1,4-dioxane. One of these acts like an ether an...
- (a) Simple aminoacetals hydrolyze quickly and easily in dilute acid. Propose a mechanism for hydrolysis of the...
- Hydration of an aldehyde is also catalyzed by hydroxide ion. Propose a mechanism for the reaction.
- Which of the following are a. hemiacetals? b. acetals? c. hydrates? 1. (CH3)2COCH3(OH)
- Which of the following are a. hemiacetals? b. acetals? c. hydrates? 3. (OCH3)2CH3CH
- Identify A through O:

