- 1. A Review of General Chemistry
- Summary
- Intro to Organic Chemistry
- Atomic Structure
- Wave Function
- Molecular Orbitals
- Sigma and Pi Bonds
- Octet Rule
- Bonding Preferences
- Formal Charges
- Skeletal Structure
- Lewis Structure
- Condensed Structural Formula
- Degrees of Unsaturation
- Constitutional Isomers
- Resonance Structures
- Hybridization
- Molecular Geometry
- Electronegativity
- 2. Molecular Representations
- 3. Acids and Bases
- 4. Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
- IUPAC Naming
- Alkyl Groups
- Naming Cycloalkanes
- Naming Bicyclic Compounds
- Naming Alkyl Halides
- Naming Alkenes
- Naming Alcohols
- Naming Amines
- Cis vs Trans
- Conformational Isomers
- Newman Projections
- Drawing Newman Projections
- Barrier To Rotation
- Ring Strain
- Axial vs Equatorial
- Cis vs Trans Conformations
- Equatorial Preference
- Chair Flip
- Calculating Energy Difference Between Chair Conformations
- A-Values
- Decalin
- 5. Chirality
- Constitutional Isomers vs. Stereoisomers
- Chirality
- Test 1:Plane of Symmetry
- Test 2:Stereocenter Test
- R and S Configuration
- Enantiomers vs. Diastereomers
- Atropisomers
- Meso Compound
- Test 3:Disubstituted Cycloalkanes
- What is the Relationship Between Isomers?
- Fischer Projection
- R and S of Fischer Projections
- Optical Activity
- Enantiomeric Excess
- Calculations with Enantiomeric Percentages
- Non-Carbon Chiral Centers
- 6. Thermodynamics and Kinetics
- 7. Substitution Reactions
- 8. Elimination Reactions
- 9. Alkenes and Alkynes
- 10. Addition Reactions
- Addition Reaction
- Markovnikov
- Hydrohalogenation
- Acid-Catalyzed Hydration
- Oxymercuration
- Hydroboration
- Hydrogenation
- Halogenation
- Halohydrin
- Carbene
- Epoxidation
- Epoxide Reactions
- Dihydroxylation
- Ozonolysis
- Ozonolysis Full Mechanism
- Oxidative Cleavage
- Alkyne Oxidative Cleavage
- Alkyne Hydrohalogenation
- Alkyne Halogenation
- Alkyne Hydration
- Alkyne Hydroboration
- 11. Radical Reactions
- 12. Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides and Thiols
- Alcohol Nomenclature
- Naming Ethers
- Naming Epoxides
- Naming Thiols
- Alcohol Synthesis
- Leaving Group Conversions - Using HX
- Leaving Group Conversions - SOCl2 and PBr3
- Leaving Group Conversions - Sulfonyl Chlorides
- Leaving Group Conversions Summary
- Williamson Ether Synthesis
- Making Ethers - Alkoxymercuration
- Making Ethers - Alcohol Condensation
- Making Ethers - Acid-Catalyzed Alkoxylation
- Making Ethers - Cumulative Practice
- Ether Cleavage
- Alcohol Protecting Groups
- t-Butyl Ether Protecting Groups
- Silyl Ether Protecting Groups
- Sharpless Epoxidation
- Thiol Reactions
- Sulfide Oxidation
- 13. Alcohols and Carbonyl Compounds
- 14. Synthetic Techniques
- 15. Analytical Techniques:IR, NMR, Mass Spect
- Purpose of Analytical Techniques
- Infrared Spectroscopy
- Infrared Spectroscopy Table
- IR Spect:Drawing Spectra
- IR Spect:Extra Practice
- NMR Spectroscopy
- 1H NMR:Number of Signals
- 1H NMR:Q-Test
- 1H NMR:E/Z Diastereoisomerism
- H NMR Table
- 1H NMR:Spin-Splitting (N + 1) Rule
- 1H NMR:Spin-Splitting Simple Tree Diagrams
- 1H NMR:Spin-Splitting Complex Tree Diagrams
- 1H NMR:Spin-Splitting Patterns
- NMR Integration
- NMR Practice
- Carbon NMR
- Structure Determination without Mass Spect
- Mass Spectrometry
- Mass Spect:Fragmentation
- Mass Spect:Isotopes
- 16. Conjugated Systems
- Conjugation Chemistry
- Stability of Conjugated Intermediates
- Allylic Halogenation
- Reactions at the Allylic Position
- Conjugated Hydrohalogenation (1,2 vs 1,4 addition)
- Diels-Alder Reaction
- Diels-Alder Forming Bridged Products
- Diels-Alder Retrosynthesis
- Molecular Orbital Theory
- Drawing Atomic Orbitals
- Drawing Molecular Orbitals
- HOMO LUMO
- Orbital Diagram:3-atoms- Allylic Ions
- Orbital Diagram:4-atoms- 1,3-butadiene
- Orbital Diagram:5-atoms- Allylic Ions
- Orbital Diagram:6-atoms- 1,3,5-hexatriene
- Orbital Diagram:Excited States
- Pericyclic Reaction
- Thermal Cycloaddition Reactions
- Photochemical Cycloaddition Reactions
- Thermal Electrocyclic Reactions
- Photochemical Electrocyclic Reactions
- Cumulative Electrocyclic Problems
- Sigmatropic Rearrangement
- Cope Rearrangement
- Claisen Rearrangement
- 17. Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
- 18. Aromaticity
- 19. Reactions of Aromatics: EAS and Beyond
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
- Benzene Reactions
- EAS:Halogenation Mechanism
- EAS:Nitration Mechanism
- EAS:Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Mechanism
- EAS:Friedel-Crafts Acylation Mechanism
- EAS:Any Carbocation Mechanism
- Electron Withdrawing Groups
- EAS:Ortho vs. Para Positions
- Acylation of Aniline
- Limitations of Friedel-Crafts Alkyation
- Advantages of Friedel-Crafts Acylation
- Blocking Groups - Sulfonic Acid
- EAS:Synergistic and Competitive Groups
- Side-Chain Halogenation
- Side-Chain Oxidation
- Reactions at Benzylic Positions
- Birch Reduction
- EAS:Sequence Groups
- EAS:Retrosynthesis
- Diazo Replacement Reactions
- Diazo Sequence Groups
- Diazo Retrosynthesis
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution
- Benzyne
- 20. Phenols
- 21. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition
- Naming Aldehydes
- Naming Ketones
- Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
- Oxidation of Alcohols
- Ozonolysis
- DIBAL
- Alkyne Hydration
- Nucleophilic Addition
- Cyanohydrin
- Organometallics on Ketones
- Overview of Nucleophilic Addition of Solvents
- Hydrates
- Hemiacetal
- Acetal
- Acetal Protecting Group
- Thioacetal
- Imine vs Enamine
- Addition of Amine Derivatives
- Wolff Kishner Reduction
- Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation
- Acid Chloride to Ketone
- Nitrile to Ketone
- Wittig Reaction
- Ketone and Aldehyde Synthesis Reactions
- 22. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: NAS
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
- Naming Carboxylic Acids
- Diacid Nomenclature
- Naming Esters
- Naming Nitriles
- Acid Chloride Nomenclature
- Naming Anhydrides
- Naming Amides
- Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
- Carboxylic Acid to Acid Chloride
- Fischer Esterification
- Acid-Catalyzed Ester Hydrolysis
- Saponification
- Transesterification
- Lactones, Lactams and Cyclization Reactions
- Carboxylation
- Decarboxylation Mechanism
- Review of Nitriles
- 23. The Chemistry of Thioesters, Phophate Ester and Phosphate Anhydrides
- 24. Enolate Chemistry: Reactions at the Alpha-Carbon
- Tautomerization
- Tautomers of Dicarbonyl Compounds
- Enolate
- Acid-Catalyzed Alpha-Halogentation
- Base-Catalyzed Alpha-Halogentation
- Haloform Reaction
- Hell-Volhard-Zelinski Reaction
- Overview of Alpha-Alkylations and Acylations
- Enolate Alkylation and Acylation
- Enamine Alkylation and Acylation
- Beta-Dicarbonyl Synthesis Pathway
- Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis
- Malonic Ester Synthesis
- 25. Condensation Chemistry
- 26. Amines
- 27. Heterocycles
- Nomenclature of Heterocycles
- Acid-Base Properties of Nitrogen Heterocycles
- Reactions of Pyrrole, Furan, and Thiophene
- Directing Effects in Substituted Pyrroles, Furans, and Thiophenes
- Addition Reactions of Furan
- EAS Reactions of Pyridine
- SNAr Reactions of Pyridine
- Side-Chain Reactions of Substituted Pyridines
- 28. Carbohydrates
- Monosaccharide
- Monosaccharides - D and L Isomerism
- Monosaccharides - Drawing Fischer Projections
- Monosaccharides - Common Structures
- Monosaccharides - Forming Cyclic Hemiacetals
- Monosaccharides - Cyclization
- Monosaccharides - Haworth Projections
- Mutarotation
- Epimerization
- Monosaccharides - Aldose-Ketose Rearrangement
- Monosaccharides - Alkylation
- Monosaccharides - Acylation
- Glycoside
- Monosaccharides - N-Glycosides
- Monosaccharides - Reduction (Alditols)
- Monosaccharides - Weak Oxidation (Aldonic Acid)
- Reducing Sugars
- Monosaccharides - Strong Oxidation (Aldaric Acid)
- Monosaccharides - Oxidative Cleavage
- Monosaccharides - Osazones
- Monosaccharides - Kiliani-Fischer
- Monosaccharides - Wohl Degradation
- Monosaccharides - Ruff Degradation
- Disaccharide
- Polysaccharide
- 29. Amino Acids
- Proteins and Amino Acids
- L and D Amino Acids
- Polar Amino Acids
- Amino Acid Chart
- Acid-Base Properties of Amino Acids
- Isoelectric Point
- Amino Acid Synthesis: HVZ Method
- Synthesis of Amino Acids: Acetamidomalonic Ester Synthesis
- Synthesis of Amino Acids: N-Phthalimidomalonic Ester Synthesis
- Synthesis of Amino Acids: Strecker Synthesis
- Reactions of Amino Acids: Esterification
- Reactions of Amino Acids: Acylation
- Reactions of Amino Acids: Hydrogenolysis
- Reactions of Amino Acids: Ninhydrin Test
- 30. Peptides and Proteins
- Peptides
- Primary Protein Structure
- Secondary Protein Structure
- Tertiary Protein Structure
- Disulfide Bonds
- Quaternary Protein Structure
- Summary of Protein Structure
- Intro to Peptide Sequencing
- Peptide Sequencing: Partial Hydrolysis
- Peptide Sequencing: Partial Hydrolysis with Cyanogen Bromide
- Peptide Sequencing: Edman Degradation
- Merrifield Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis
- 31. Catalysis in Organic Reactions
- 32. Lipids
- 33. The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
- Intro to Metabolism
- ATP and Energy
- Intro to Coenzymes
- Coenzymes in Metabolism
- Energy Production in Biochemical Pathways
- Intro to Glycolysis
- Catabolism of Carbohydrates: Glycolysis
- Glycolysis Summary
- Pyruvate Oxidation (Simplified)
- Anaerobic Respiration
- Catabolism of Fats: Glycerol Metabolism
- Intro to Citric Acid Cycle
- Structures of the Citric Acid Cycle
- The Citric Acid Cycle
- 34. Nucleic Acids
- 35. Transition Metals
- Electron Configuration of Elements
- Coordination Complexes
- Ligands
- Electron Counting
- The 18 and 16 Electron Rule
- Cross-Coupling General Reactions
- Heck Reaction
- Stille Reaction
- Suzuki Reaction
- Sonogashira Coupling Reaction
- Fukuyama Coupling Reaction
- Kumada Coupling Reaction
- Negishi Coupling Reaction
- Buchwald-Hartwig Amination Reaction
- Eglinton Reaction
- Catalytic Allylic Alkylation
- Alkene Metathesis
- 36. Synthetic Polymers
- Introduction to Polymers
- Chain-Growth Polymers
- Radical Polymerization
- Cationic Polymerization
- Anionic Polymerization
- Polymer Stereochemistry
- Ziegler-Natta Polymerization
- Copolymers
- Step-Growth Polymers
- Step-Growth Polymers: Urethane
- Step-Growth Polymers: Polyurethane Mechanism
- Step-Growth Polymers: Epoxy Resin
- Polymers Structure and Properties
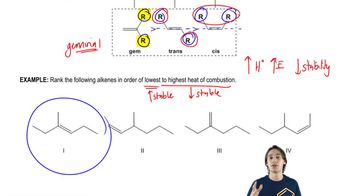
9. Alkenes and Alkynes
Alkene Stability
Practice this topic
- Textbook Question
Rank the following compounds from most stable to least stable:
trans-3-hexene, cis-3-hexene, cis-2,5-dimethyl-3-hexene, (Z)-3,4-dimethyl-3-hexene
1290views - Textbook Question
The energy difference between cis- and trans-but-2-ene is about 4 kJ/mol; however, the trans isomer of 4,4-dimethylpent-2-ene is nearly 16 kJ/mol more stable than the cis isomer. Explain this large difference.
1857views - Textbook Question
For each set of isomers, choose the isomer that you expect to be most stable and the isomer you expect to be least stable.
(a)
1412views - Textbook Question
Explain why each of the following alkenes is stable or unstable.
(a) 1,2-dimethylcyclopentene
(b) trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopentene
(c) trans-3,4-dimethylcyclopentene
(d) trans-1,2-dimethylcyclodecene
1390views - Multiple Choice
When the alkyne is treated with ozone followed by water, how many carboxylic acid products are formed?
74views - Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the correct structure for ?
61views - Multiple Choice
Which of the following alkenes is the most stable?
64views - Multiple Choice
Which of the following alkenes is the most stable?
68views