Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amino Acid Structure
Amino acids are organic compounds characterized by a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group). The R group determines the specific properties and identity of the amino acid, influencing its role in protein synthesis and function.
Recommended video:
Synthesis of Amino Acids
The synthesis of amino acids often involves the formation of the amino and carboxyl functional groups from suitable starting materials. Common methods include the Strecker synthesis, which uses aldehydes, ammonium chloride, and cyanide, and the Gabriel synthesis, which employs phthalimide and alkyl halides to introduce the amino group.
Recommended video:
Synthesis of Amino Acids: Strecker Synthesis Example 1
Reagents in Organic Synthesis
Reagents are substances used in chemical reactions to facilitate the transformation of reactants into products. In amino acid synthesis, reagents such as acids, bases, and coupling agents are crucial for forming peptide bonds and modifying functional groups, enabling the construction of the amino acid structure from simpler precursors.
Recommended video:
Synthesis of Amino Acids: Strecker Synthesis Example 1

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: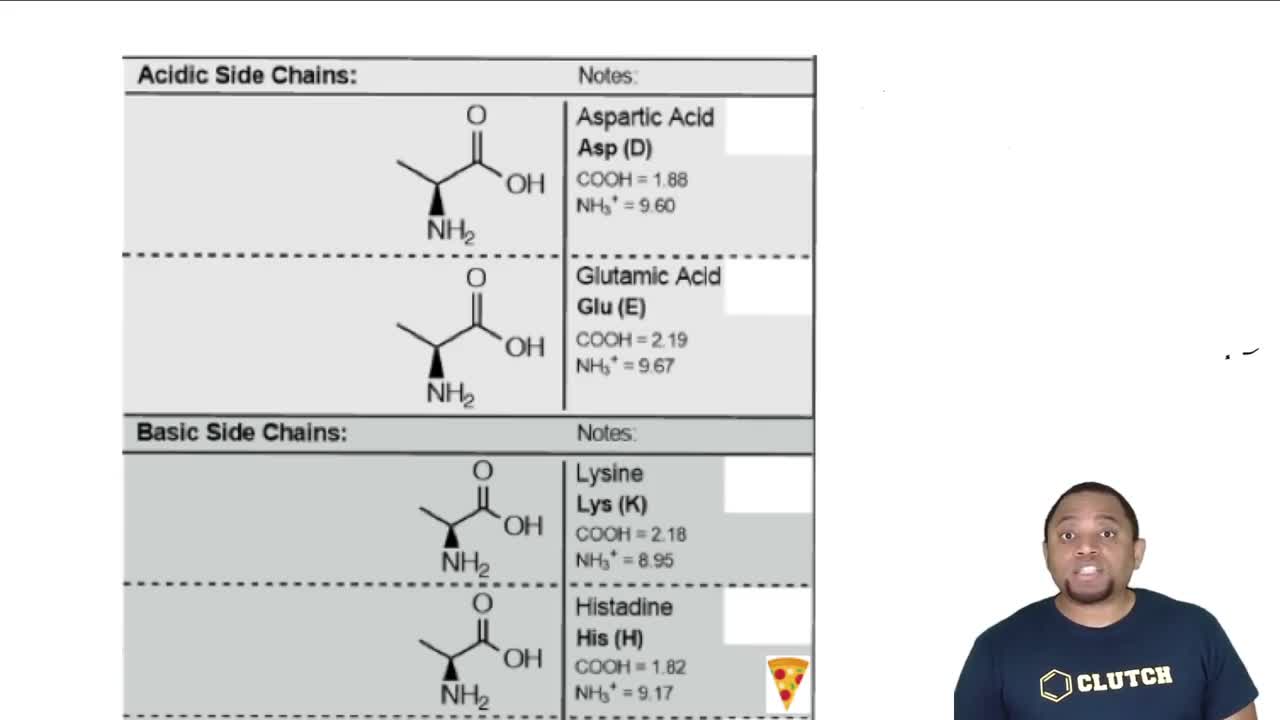



 9:34m
9:34m