Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
b-Diester
A b-diester is a type of organic compound that contains two ester functional groups (-COOR) connected by a carbon chain. The 'b' indicates that the ester groups are located at the 1 and 3 positions of a three-carbon chain, making it a symmetrical structure. This compound is significant in organic synthesis and can be used in various reactions, such as the synthesis of cyclic compounds.
Recommended video:
Diesters (Dieckmann Condensation)
Esterification
Esterification is the chemical reaction that forms an ester from an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, typically in the presence of an acid catalyst. This process involves the nucleophilic attack of the alcohol's hydroxyl group on the carbonyl carbon of the acid, leading to the release of water. Understanding esterification is crucial for synthesizing b-diesters and other ester compounds.
Recommended video:
Reactions of Amino Acids: Esterification Concept 1
Synthesis of b-Diesters
The synthesis of b-diesters can be achieved through various methods, including the reaction of a dicarbonyl compound with alcohols or through the esterification of a diacid. This process often involves controlling reaction conditions to ensure the formation of the desired b-diester product. Familiarity with synthetic pathways is essential for effectively creating and utilizing b-diesters in organic chemistry.
Recommended video:
Synthesis of Amino Acids: Strecker Synthesis Example 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution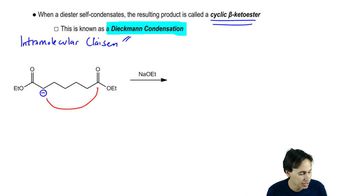



 2:39m
2:39m