Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isomerism
Isomerism refers to the phenomenon where compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. In the case of 1,2-dichloroethene, the two isomers are geometric isomers, specifically cis and trans isomers, which differ in the spatial arrangement of the chlorine atoms around the double bond.
Recommended video:
Monosaccharides - D and L Isomerism
Dipole Moment
A dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule. It is a vector quantity, with both magnitude and direction. Molecules with symmetrical charge distribution, like the trans isomer of 1,2-dichloroethene, can have a net dipole moment of zero, while asymmetrical ones, like the cis isomer, have a non-zero dipole moment.
Recommended video:
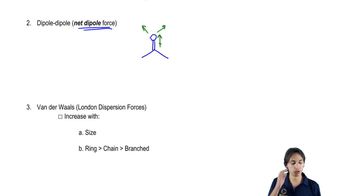
How dipole-dipole forces work.
Cis-Trans Isomerism
Cis-trans isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism where the relative orientation of functional groups within a molecule differs. In 1,2-dichloroethene, the cis isomer has both chlorine atoms on the same side of the double bond, resulting in a net dipole moment, while the trans isomer has them on opposite sides, canceling out the dipole moment.
Recommended video:
Is the following cyclohexane cis or trans?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: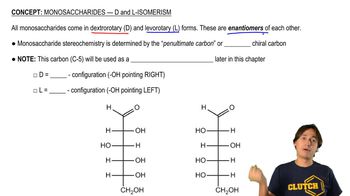


 11:33m
11:33m