Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Skeletal Structures
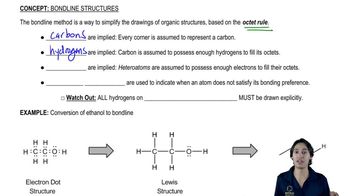
Skeletal structures, or line-angle formulas, are simplified representations of organic molecules where carbon atoms are implied at the ends of lines and intersections. Hydrogen atoms attached to carbons are usually omitted for clarity. This notation allows chemists to visualize the molecular framework quickly, focusing on functional groups and connectivity.
Recommended video:
How bondline is different from Lewis Structures.
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In the case of CH3COOH, the carboxylic acid functional group (-COOH) is crucial, as it defines the compound's acidic properties and reactivity. Recognizing functional groups is essential for predicting the behavior of organic compounds.
Recommended video:
Identifying Functional Groups
Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH). They are known for their acidic properties due to the ability of the carboxyl group to donate a proton (H+) in solution. Understanding the structure and properties of carboxylic acids, like acetic acid (CH3COOH), is fundamental in organic chemistry, as they are prevalent in various biological and industrial processes.
Recommended video:
Carboxylic Acids Nomenclature