Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Resonance
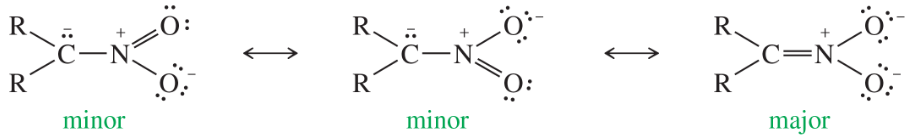
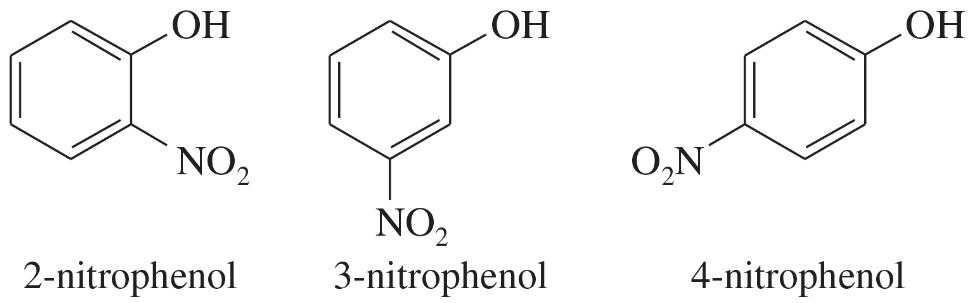
Resonance is a concept in organic chemistry that describes the delocalization of electrons in molecules where the bonding cannot be expressed by a single Lewis structure. Instead, multiple structures, known as resonance structures, are used to represent the molecule's electron distribution. This delocalization stabilizes the molecule, as seen in nitrophenols, where the negative charge can be spread over multiple atoms.
Recommended video:
Drawing Resonance Structures
Acidity and Conjugate Bases
Acidity in organic compounds is often determined by the stability of their conjugate bases. A more stable conjugate base corresponds to a stronger acid. In the case of nitrophenols, the presence of the nitro group enhances the stability of the phenoxide ion through resonance, making the compound more acidic compared to phenol, which lacks such stabilization.
Recommended video:
Equilibrium constant and conjugates.
Electronegative Substituents
Electronegative substituents, like nitro groups, can significantly influence the acidity of organic compounds. They stabilize negative charges through resonance or inductive effects, thereby increasing acidity. In nitrophenols, the nitro group withdraws electron density, facilitating the stabilization of the phenoxide ion and enhancing the overall acidity of the compound.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 3:15m
3:15m