Compare and contrast the following:
a. simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion
b. active transport and facilitated diffusion
c. active transport and group translocation
 Tortora 14th Edition
Tortora 14th Edition Ch. 4 - Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Ch. 4 - Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Problem 4.7a
Problem 4.7a Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Compare and contrast the following:
a. simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion
b. active transport and facilitated diffusion
c. active transport and group translocation
Which of the following is false about fimbriae?
a. They are composed of protein.
b. They may be used for attachment.
c. They are found on gram-negative cells.
d. They are composed of pilin.
e. They may be used for motility.
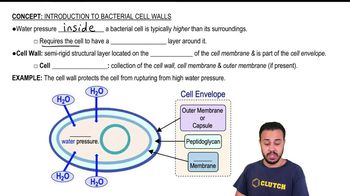
Answer the following questions using the diagrams provided, which represent cross sections of bacterial cell walls.
a. Which diagram represents a gram-positive bacterium? How can you tell? <IMAGE>
b. Explain how the Gram stain works to distinguish these two types of cell walls.
c. Why does penicillin have no effect on most gram-negative cells?
d. How do essential molecules enter cells through each wall?
e. Which cell wall is toxic to humans?
Starch is readily metabolized by many cells, but a starch molecule is too large to cross the plasma membrane. How does a cell obtain the glucose molecules from a starch polymer? How does the cell transport these glucose molecules across the plasma membrane?
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
a. metachromatic granules—stored phosphates
b. polysaccharide granules—stored starch
c. lipid inclusions—poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid
d. sulfur granules—energy reserve
e. ribosomes—protein storage
You have isolated a motile, gram-positive cell with no visible nucleus. You can assume this cell has
a. ribosomes.
b. mitochondria.
c. an endoplasmic reticulum.
d. a Golgi complex.
e. all of the above