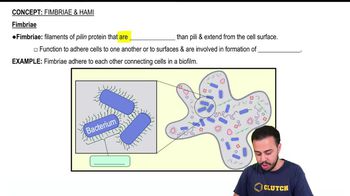
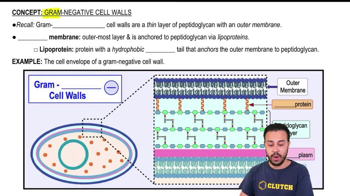
Which of the following statements best describes what happens to a cell exposed to polymyxins that destroy phospholipids?
a. In an isotonic solution, nothing will happen.
b. In a hypotonic solution, the cell will lyse.
c. Water will move into the cell.
d. Intracellular contents will leak from the cell.
e. Any of the above might happen.