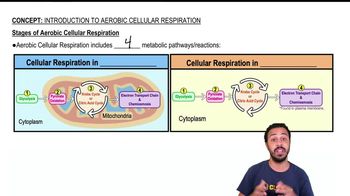
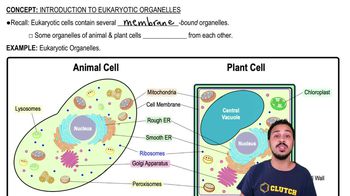
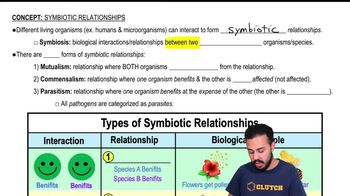
Use the following choices to answer questions 2–4.
a. No change will result; the solution is isotonic.
b. Water will move into the cell.
c. Water will move out of the cell.
d. The cell will undergo osmotic lysis.
e. Sucrose will move into the cell from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration.
Which statement best describes what happens when a gram-positive bacterium is placed in distilled water and penicillin?