Classify the following types of chemical reactions.
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Classify the following types of chemical reactions.
<IMAGE>
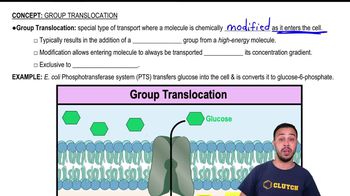
Bacteria use the enzyme urease to obtain nitrogen in a form they can use from urea in the following reaction:
<IMAGE>
What purpose does the enzyme serve in this reaction? What type of reaction is this?
DRAW IT The artificial sweetener aspartame, or NutraSweet®, is made by joining aspartic acid to methylated phenylalanine, as shown in the following.
<IMAGE>
a. What types of molecules are aspartic acid and phenylalanine?
b. What direction is the hydrolysis reaction (left to right or right to left)?
c. What direction is the dehydration synthesis reaction?
d. Circle the atoms involved in the formation of water.
e. Identify the peptide bond.
Use the following diagrams (a), (b), and (c) for question 1.
<IMAGE>
Name pathways diagrammed in parts (a), (b), and (c) of the figure.
a. Show where glycerol is catabolized and where fatty acids are catabolized.
b. Show where glutamic acid (an amino acid) is catabolized:
<IMAGE>
c. Show how these pathways are related.
d. Where is ATP required in pathways (a) and (b)?
e. Where is CO₂ released in pathways (b) and (c)?
f. Show where a long-chain hydrocarbon such as petroleum is catabolized.
g. Where is NADH (or FADH₂ or NADPH) used and produced in these pathways?
h. Identify four places where anabolic and catabolic pathways are integrated.
DRAW IT What nutritional type is a colorless microbe that uses the Calvin-Benson cycle, uses H₂ as the electron donor to its ETC, and uses elemental S as the final electron acceptor in the ETC?