Bacteria use the enzyme urease to obtain nitrogen in a form they can use from urea in the following reaction:
<IMAGE>
What purpose does the enzyme serve in this reaction? What type of reaction is this?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
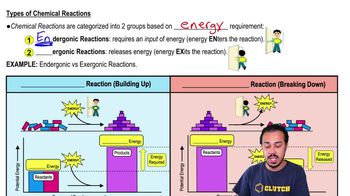


Bacteria use the enzyme urease to obtain nitrogen in a form they can use from urea in the following reaction:
<IMAGE>
What purpose does the enzyme serve in this reaction? What type of reaction is this?
The best definition of ATP is that it is
a. a molecule stored for food use.
b. a molecule that supplies energy to do work.
c. a molecule stored for an energy reserve.
d. a molecule used as a source of phosphate.
DRAW IT The artificial sweetener aspartame, or NutraSweet®, is made by joining aspartic acid to methylated phenylalanine, as shown in the following.
<IMAGE>
a. What types of molecules are aspartic acid and phenylalanine?
b. What direction is the hydrolysis reaction (left to right or right to left)?
c. What direction is the dehydration synthesis reaction?
d. Circle the atoms involved in the formation of water.
e. Identify the peptide bond.