Match the following choices to the statements in questions 5–7:
a. IgA
b. IgD
c. IgE
d. IgG
e. IgM
Antibodies that protect the fetus and newborn.
 Tortora 14th Edition
Tortora 14th Edition Ch. 17 - Adaptive Immunity: Specific Defenses of the Host
Ch. 17 - Adaptive Immunity: Specific Defenses of the Host Problem 17.7a
Problem 17.7a Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

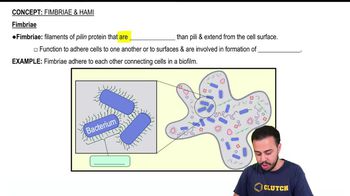
Match the following choices to the statements in questions 5–7:
a. IgA
b. IgD
c. IgE
d. IgG
e. IgM
Antibodies that protect the fetus and newborn.
DRAW IT
a. In the following graph, at time A the host was injected with tetanus toxoid. Show the response to a booster dose at time B.
b. Draw the antibody response of this same individual to exposure to a new antigen at time B.
<IMAGE>
Match the following choices to the statements in questions 5–7:
a. IgA
b. IgD
c. IgE
d. IgG
e. IgM
The first antibodies synthesized; especially effective against microorganisms.
Match the following choices to the statements in questions 5–7:
a. IgA
b. IgD
c. IgE
d. IgG
e. IgM
Antibodies that are bound to mast cells and involved in allergic reactions.
Explain why a person who recovers from a disease can attend others with the disease without fear of contracting it.
Put the following in the correct sequence to elicit an antibody response: (1) TH cell produces cytokines; (2) B cell contacts antigen; (3) antigen fragment goes to surface of the B cell; (4) TH recognizes antigen fragment and MHC; (5) B cell proliferates.
a. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
b. 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
c. 3, 4, 5, 1, 2
d. 2, 3, 4, 1, 5
e. 4, 5, 3, 1, 2