Identify the viral family that infects skin, mucosa, and nerve cells; causes infections that can recur because of latency; and has polyhedral geometry.
List the four properties that define a virus. What is a virion?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Properties of Viruses
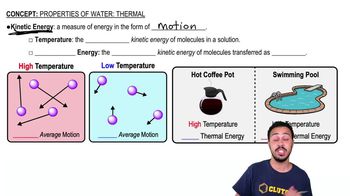
Virion Structure
Viral Replication

Place the following in the most likely order for biosynthesis of a bacteriophage: (1) phage lysozyme; (2) mRNA; (3) DNA; (4) viral proteins; (5) DNA polymerase.
a. 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
b. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
c. 5, 3, 4, 2, 1
d. 3, 5, 2, 4, 1
e. 2, 5, 3, 4, 1
A viral species is not defined on the basis of the disease symptoms it causes. The best example of this is
a. polio.
b. rabies.
c. hepatitis.
d. chickenpox and shingles.
e. measles.
The molecule serving as mRNA can be incorporated in the newly synthesized virus
capsids of all of the following except
a. + strand RNA picornaviruses.
b. + strand RNA togaviruses.
c. strand RNA rhabdoviruses.
d. double-stranded RNA reoviruses.
e. Rotavirus.
A virus with RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
a. synthesizes DNA from an RNA template.
b. synthesizes double-stranded RNA from an RNA template.
c. synthesizes double-stranded RNA from a DNA template.
d. transcribes mRNA from DNA.
e. none of the above
Label the principal events of attachment, biosynthesis, entry, and maturation of a + stranded RNA virus. Draw in uncoating. <IMAGE>
