Plant viruses can’t penetrate intact plant cells because (a) ________; therefore, they enter cells by (b) ________. Plant viruses can be cultured in (c) ________.
Define the following terms, and give an example of how each reaction is used diagnostically:
a. viral hemagglutination
b. hemagglutination inhibition
c. passive agglutination
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Viral Hemagglutination

Hemagglutination Inhibition
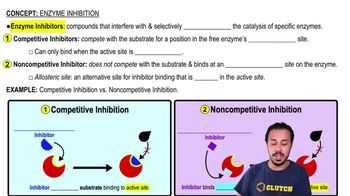
Passive Agglutination
Which of the following does not initiate DNA synthesis?
a. a double-stranded DNA virus (Poxviridae)
b. a DNA virus with reverse transcriptase (Hepadnaviridae)
c. an RNA virus with reverse transcriptase (Retroviridae)
d. a single-stranded RNA virus (Togaviridae)
e. none of the above
In an agglutination test, eight serial dilutions to determine antibody titer were set up: Tube 1 contained a 1:2 dilution; tube 2, a 1:4, and so on. If tube 5 is the last tube showing agglutination, what is the antibody titer?
a. 5
b. 1:5
c. 32
d. 1:32
Use the following choices to answer questions 7–9.
a. direct fluorescent antibody
b. indirect fluorescent antibody
c. rabies immune globulin
d. killed rabies virus
e. none of the above
Test used to identify rabies virus in the brain of a dog.
Use the following choices to answer questions 7–9.
a. direct fluorescent antibody
b. indirect fluorescent antibody
c. rabies immune globulin
d. killed rabies virus
e. none of the above
Test used to detect the presence of antibodies in a patient’s serum.
The 19 in COVID-19 signifies that
a. this is the 19th coronavirus epidemic.
b. this is 19th known coronavirus.
c. there are 19 strains of Betacoronavirus.
d. the virus was identified in 2019.
e. the symptoms last for 19 days.
