Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Dioecious
The term 'dioecious' refers to a reproductive strategy in which individual organisms are distinctly male or female. In dioecious species, separate sexes are necessary for reproduction, as they rely on mating between males and females to produce offspring. This contrasts with hermaphroditic organisms, which possess both male and female reproductive organs.
Phylum Nematoda
Roundworms belong to the phylum Nematoda, which is characterized by their elongated, cylindrical bodies and a complete digestive system. Nematodes are incredibly diverse and can be found in various environments, including soil, freshwater, and marine ecosystems. They play significant roles in nutrient cycling and can also be important as parasites in plants and animals.
Recommended video:
Reproductive Strategies in Animals
Reproductive strategies in animals encompass the various methods by which species reproduce and ensure the survival of their offspring. These strategies can include dioecy, hermaphroditism, and asexual reproduction. Understanding these strategies is crucial for studying biodiversity, evolutionary biology, and the ecological roles of different organisms.
Recommended video:
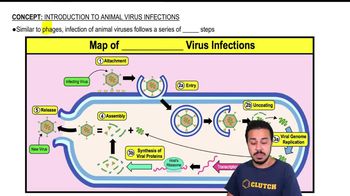
Introduction to Animal Virus Infections