Textbook Question
Under what conditions can the saprophytes Aspergillus and Rhizopus cause infections?
135
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

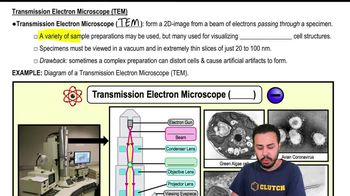

Under what conditions can the saprophytes Aspergillus and Rhizopus cause infections?
Complete the following table:
<IMAGE>
NAME IT Cysts of this flagellated organism survive in water; when ingested, the trophozoite grows in the intestine, causing diarrhea.
Use the following choices to answer questions 7–10:
a. Campylobacter
b. Cryptosporidium
c. Escherichia
d. Salmonella
e. Trichinella
This microbe is frequently transmitted to humans via raw eggs.
Complete the following table:
<IMAGE>
DRAW IT Identify the site colonized by the following organisms: E. granulosus, E. vermicularis, Giardia, H. pylori, hepatitis B virus, mumps virus, Rotavirus, Salmonella, Shigella, Streptococcus mutans, Trichinella spiralis, Trichuris.
<IMAGE>