_______________________ is a process that uses energy from nutrients to fuel an electron transport chain to make ATP.
Use this pathway schematic to answer questions a through d.
a. Which enzyme carries out a redox reaction? In this reaction, what is being reduced and what is being oxidized?
b. Which enzyme would be the most likely to be regulated by feedback inhibition?
c. What is the end product of this pathway?
d. Which enzyme carries out substrate-level phosphorylation?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Redox Reactions

Feedback Inhibition

Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
The _______________________ test detects if an organism can convert hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. The test result is usually _______________________ in anaerobic microbes and usually _______________________ in aerobic microbes. You know the test is positive by _______________________.
The photo shows an organism growing in glucose fermentation broth. What can you conclude about this specimen with regard to its ability (or lack thereof) to ferment the sugar sucrose? Explain your answer.
<IMAGE>
Match the term to the statement. (Some terms will be used more than once.)
<IMAGE>
Rank the following from the most ATP that could be made to the least ATP that could be made: (NCLEX/HESI/TEAS)
a. 1 glucose molecule processed via a fermentation pathway (consider that glycolysis is the first stage of the process)
b. A lipid made of glycerol and three 10-carbon fatty acid chains entering cellular respiration
c. 1 glucose molecule entering the Entner–Doudoroff pathway
d. 1 glucose molecule entering cellular respiration
Indicate the true statements about ATP, and then reword the false statements so that they are true.
a. ATP is made using anabolic reactions.
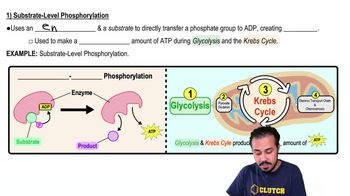
b. Substrate-level phosphorylation converts ATP to ADP.
c. ATP is commonly used by cells to store energy.
d. ATP is used to jump-start cellular respiration.
e. Catabolic reactions are used to make ATP.
f. In cellular respiration, the most ATP is made by glycolysis.
g. ATP can be made by phosphorylating ADP.
