Which of the following is false? (NCLEX/HESI/TEAS)
a. ATP is used to fuel cellular work.
b. ATP is a specialized ribonucleotide.
c. Energy is released from ATP by breaking off phosphate groups.
d. ATP is used to fuel exergonic reactions.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Which of the following is false? (NCLEX/HESI/TEAS)
a. ATP is used to fuel cellular work.
b. ATP is a specialized ribonucleotide.
c. Energy is released from ATP by breaking off phosphate groups.
d. ATP is used to fuel exergonic reactions.
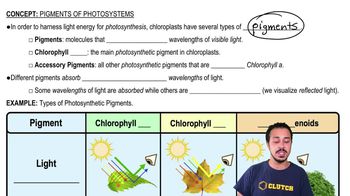
Label each reactant and product in the reactions as reduced or oxidized (X is a theoretical molecule or atom).
<IMAGE>
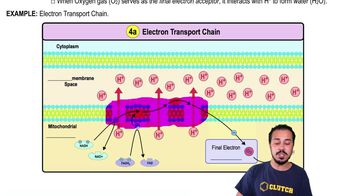
_______________________ is a process that uses energy from nutrients to fuel an electron transport chain to make ATP.
The _______________________ test detects if an organism can convert hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. The test result is usually _______________________ in anaerobic microbes and usually _______________________ in aerobic microbes. You know the test is positive by _______________________.
The photo shows an organism growing in glucose fermentation broth. What can you conclude about this specimen with regard to its ability (or lack thereof) to ferment the sugar sucrose? Explain your answer.
<IMAGE>