Pick which statements are true, then correct all false statements, so they are also true.
a. Redness, pain, fever, and swelling characterize inflammation.
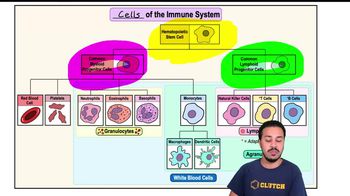
b. Granulocytes include monocytes and lymphocytes.
c. Pyrogens induce fever.
d. Adaptive and innate immune responses are completely independent from one another.
e. The innate immune responses occur faster than adaptive responses.
f. Monocytes are highly phagocytic cells.
g. Complement cascades share the same outcomes: opsonization, cytolysis, and fever.