What happens to the carbon atoms in sugar catabolized by Escherichia coli?
Ch. 5 - Microbial Metabolism
Chapter 5, Problem 5.13a
Which of the following does not affect the function of enzymes?
a. ubiquinone
b. substrate concentration
c. temperature
d. competitive inhibitors
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in cells.
Identify factors that typically affect enzyme activity: substrate concentration, temperature, pH, and inhibitors.
Recognize that competitive inhibitors are molecules that bind to the active site of an enzyme, preventing substrate binding, thus affecting enzyme function.
Acknowledge that temperature affects enzyme activity by influencing molecular movement and enzyme stability.
Consider that ubiquinone is a coenzyme involved in electron transport, not directly affecting enzyme activity in the context of this question.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Enzyme Function
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in cells by lowering the activation energy required. Their function can be influenced by various factors, including substrate concentration, temperature, and the presence of inhibitors. Understanding how these factors affect enzyme activity is crucial for grasping metabolic processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Functions of Enzymes
Factors Affecting Enzymes
Several factors can influence enzyme activity, including substrate concentration, which affects the rate of reaction until saturation is reached. Temperature can alter enzyme shape and activity, while competitive inhibitors bind to the active site, preventing substrate binding. Recognizing these factors helps in understanding enzyme kinetics and regulation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
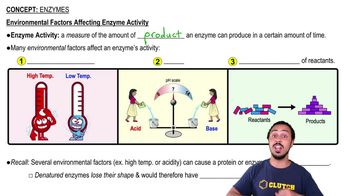
Environmental Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Ubiquinone
Ubiquinone, also known as coenzyme Q, is a lipid-soluble molecule that plays a critical role in the electron transport chain within mitochondria. Unlike the other options listed, ubiquinone does not directly affect enzyme function but rather participates in electron transfer processes. Its role is more about energy production than enzyme activity modulation.
Related Practice
Textbook Question
67
views
Textbook Question
Which of the following statements best describes ribozymes?
a. Ribozymes are proteins that aid in the production of ribosomes.
b. Ribozymes are nucleic acids that produce ribose sugars.
c. Ribozymes store enzymes in ribosomes.
d. Ribozymes process RNA molecules in eukaryotes.
71
views
Textbook Question
How do yeast cells make alcohol and cause bread to rise?
68
views
Textbook Question
Where specifically does the most significant production of ATP occur in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
63
views
Textbook Question
Most oxidation reactions in bacteria involve the _______.
a. removal of hydrogen ions and electrons
b. removal of oxygen
c. addition of hydrogen ions and electrons
d. addition of hydrogen ions
69
views
Textbook Question
Why are vitamins essential metabolic factors for microbial metabolism?
68
views
