Where specifically does the most significant production of ATP occur in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Under ideal conditions, the fermentation of one glucose molecule by a bacterium allows a net gain of how many ATP molecules?
a. 2
b. 4
c. 38
d. 0
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Fermentation
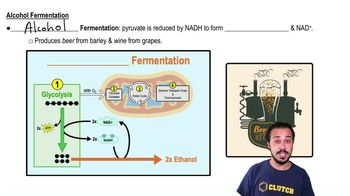
ATP Yield in Fermentation
Comparison with Aerobic Respiration

Most oxidation reactions in bacteria involve the _______.
a. removal of hydrogen ions and electrons
b. removal of oxygen
c. addition of hydrogen ions and electrons
d. addition of hydrogen ions
Why are vitamins essential metabolic factors for microbial metabolism?
A laboratory scientist notices that a certain bacterium does not utilize lactose when glucose is available in its environment. Describe a cellular regulatory mechanism that would explain this observation.
Under ideal conditions, the complete aerobic oxidation of one molecule of glucose by a bacterium allows a net gain of how many ATP molecules?
a. 2
b. 4
c. 38
d. 0
Which of the following statements about the Entner-Doudoroff pathway is false?
a. It is a series of reactions that synthesizes glucose.
b. Its products are sometimes used to determine the presence of Pseudomonas.
c. It is a pathway of chemical reactions that catabolizes glucose.
d. It is an alternative pathway to glycolysis.