Label each photograph with the type of microscope used to acquire the image.
a. _______<IMAGE>
b. _______<IMAGE>
c. _______<IMAGE>
d. _______<IMAGE>
e. _______<IMAGE>
f. _______<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

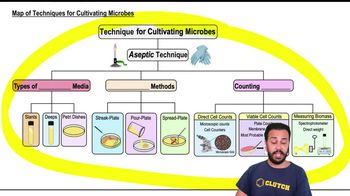

Label each photograph with the type of microscope used to acquire the image.
a. _______<IMAGE>
b. _______<IMAGE>
c. _______<IMAGE>
d. _______<IMAGE>
e. _______<IMAGE>
f. _______<IMAGE>
Explain how the principle, “electrons travel as waves,” applies to microscopy.
A nanometer is _______ than a micrometer.
a. 10 times larger
b. 10 times smaller
c. 1000 times larger
d. 1000 times smaller
Label the microscope. <IMAGE>
Critique the following definition of magnification given by a student on a microbiology test: “Magnification makes things bigger.”
Resolution is best described as the ____________.
a. ability to view something that is small
b. ability to magnify a specimen
c. ability to distinguish between two adjacent objects
d. difference between two waves of electromagnetic radiation