Textbook Question
If an objective magnifies 40× and each binocular lens magnifies 15×, the total magnification of the object being viewed is ________.
4
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
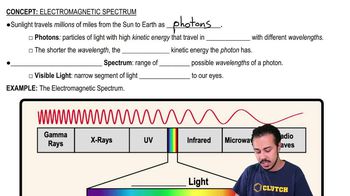

If an objective magnifies 40× and each binocular lens magnifies 15×, the total magnification of the object being viewed is ________.
Which of the following is smallest?
a. decimeter
d. millimeter
c. nanometer
d. micrometer
Label each photograph with the type of microscope used to acquire the image.
a. _______<IMAGE>
b. _______<IMAGE>
c. _______<IMAGE>
d. _______<IMAGE>
e. _______<IMAGE>
f. _______<IMAGE>
A nanometer is _______ than a micrometer.
a. 10 times larger
b. 10 times smaller
c. 1000 times larger
d. 1000 times smaller
The type of fixation developed by Koch for bacteria is _______.
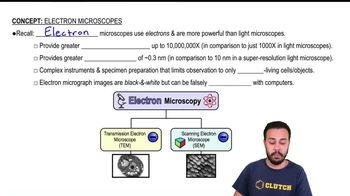
Label the microscope. <IMAGE>