________ refers to differences in intensity between two objects.
Cationic chromophores such as methylene blue ionically bond to _______(positively/negatively) charged chemicals such as DNA and proteins.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Cationic Chromophores
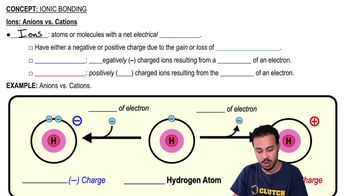
Ionic Bonding

Charge Interactions in Biology

Put the following substances in the order they are used in a Gram stain: counterstain, decolorizing agent, mordant, primary stain.
Which of the following factors is important in making an image appear larger?
a. thickness of the lens
b. curvature of the lens
c. speed of the light passing through the lens
d. all of the above
Which of the following is different between light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy?
a. magnification
b. resolution
c. wavelengths
d. all of the above
Which of the following types of microscopes produces a three- dimensional image with a shadowed appearance?
a. simple microscope
b. differential interference contrast microscope
c. fluorescence microscope
d. transmission electron microscope
Which of the following microscopes combines the greatest magnification with the best resolution?
a. confocal microscope
b. phase-contrast microscope
c. dark-field microscope
d. bright-field microscope
