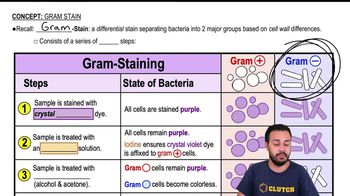
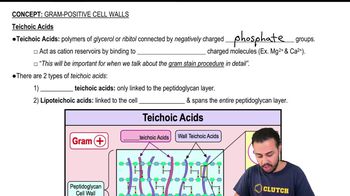
A Gram-negative cell is moving uric acid across the cytoplasmic membrane against its chemical gradient. Which of the following statements is true?
a. The exterior of the cell is probably electrically negative compared to the interior of the cell.
b. The acid probably moves by a passive means such as facilitated diffusion.
c. The acid moves by an active process such as active transport.
d. The movement of the acid requires phagocytosis.