Textbook Question
In the following molecule, label a portion that shows only primary structure; label two types of secondary structure; circle the tertiary structure.
<IMAGE>
66
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

In the following molecule, label a portion that shows only primary structure; label two types of secondary structure; circle the tertiary structure.
<IMAGE>
The atomic mass of an atom most closely approximates the sum of the masses of all its __________.
a. protons
b. isotopes
c. electrons
d protons and neutrons
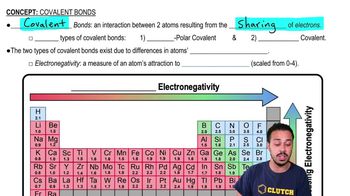
The type of chemical bond between atoms with nearly equal electronegativities is called a(n) _____________ bond.
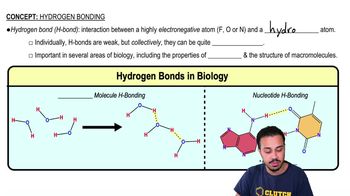
Name five properties of water that are vital to life.
Shown is the amino acid tryptophan. Put the letter “C” at the site of every carbon atom. Label the amino group, the carboxyl group, and the side group.
<IMAGE>
The principal short-term energy storage molecule in cells is __________ .