Compare and contrast the Chinese practice of variolation with Jenner’s vaccination procedure.
Monoclonal antibodies __________.
a. are produced by hybridomas
b. are secreted by clone cells
c. can be used for passive immunization
d. all of the above
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Monoclonal Antibodies
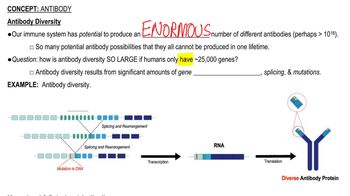
Hybridomas
Passive Immunization
Attenuation is __________.
a. the process of reducing virulence
b. a necessary step in vaccine manufacture
c. a form of variolation
d. similar to an adjuvant
An antiserum is __________.
a. an anti-antibody
b. an inactivated vaccine
c. formed of monoclonal antibodies
d. the liquid portion of blood used for immunization
The study of antibody-antigen interaction in the blood is __________.
a. attenuation
b. agglutination
c. precipitation
d. serology
Anti–human antibody antibodies are _________.
a. found in immunocompromised individuals
b. used in direct fluorescent immunoassays
c. formed by animals reacting to human immunoglobulins
d. an alternative method in ELISA
Which of the following vaccine types is commonly given with an adjuvant?
a. attenuated vaccine
b. modified live vaccine
c. chemically killed vaccine
d. immunoglobulin
