Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hormones in Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the body produces specific hormones, notably human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This hormone is secreted by the placenta shortly after a fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining. The presence of hCG in urine or blood is a key indicator of pregnancy, making it essential for the function of pregnancy tests.
Recommended video:
False Positives/Negatives
Immunoassay Technique
Pregnancy tests typically utilize an immunoassay technique, which involves antibodies that specifically bind to hCG. In a typical test, a sample of urine is applied to a test strip containing these antibodies. If hCG is present, it will bind to the antibodies, triggering a visible change, such as a color change, indicating a positive result.
Recommended video:
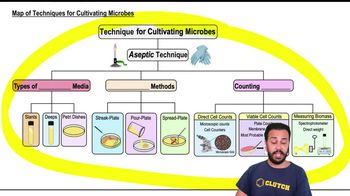
Map of Techniques for Cultivating Microbes
Detection Threshold
Pregnancy tests have a detection threshold, which is the minimum concentration of hCG required to produce a positive result. This threshold is crucial because it determines the test's sensitivity and accuracy. Tests that can detect lower levels of hCG can provide earlier results, while those with higher thresholds may miss early pregnancies.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance