Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Passive Immunotherapy
Passive immunotherapy involves the administration of pre-formed antibodies to provide immediate, but temporary, protection against pathogens. This method is often used in cases where rapid immunity is needed, such as after exposure to a toxin or in immunocompromised patients. However, the effects are short-lived, as the body does not produce its own antibodies, leading to a lack of long-term immunity.
Recommended video:
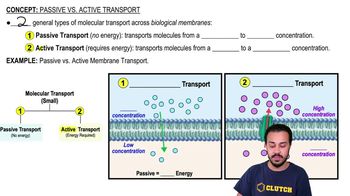
Passive vs. Active Transport
Active Immunization
Active immunization refers to the process of stimulating the immune system to produce its own antibodies through exposure to an antigen, either via vaccination or natural infection. This method leads to long-lasting immunity, as the immune system retains memory cells that can respond more effectively upon future exposure to the same pathogen. However, it may take time to develop immunity and can sometimes cause mild side effects.
Recommended video:
Immunological Memory
Immunological memory is a crucial aspect of the adaptive immune response, allowing the body to remember and respond more efficiently to previously encountered pathogens. After active immunization, memory B and T cells are generated, which can quickly recognize and combat the pathogen upon re-exposure. This concept underlines the long-term benefits of active immunization compared to the immediate but transient effects of passive immunotherapy.
Recommended video:
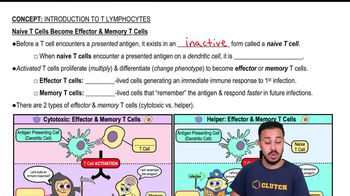
Naive T Cells Become Effector & Memory T Cells
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance