Name the cells.
a. ___________ <IMAGE> b. ___________ <IMAGE> c. ___________ <IMAGE> d. ___________ <IMAGE> e. ___________ <IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Name the cells.
a. ___________ <IMAGE> b. ___________ <IMAGE> c. ___________ <IMAGE> d. ___________ <IMAGE> e. ___________ <IMAGE>
Indicate which statements are true. Correct all false statements by changing the underlined words.
__________ Wandering macrophages experience diapedesis.
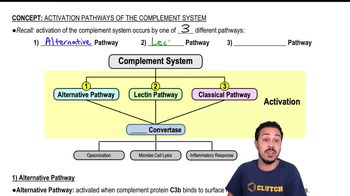
The complement system involves _____________.
a. the production of antigens and antibodies
b. serum proteins involved in nonspecific defense
c. a set of genes that distinguish foreign cells from body cells
d. the elimination of undigested remnants of microorganisms
Indicate which statements are true. Correct all false statements by changing the underlined words.
__________ Monocytes are immature macrophages.
Which of the complement fragments is inflammatory?
a. C3a
b. C4a
c. C5a
d. all of the above
Indicate which statements are true. Correct all false statements by changing the underlined words.
__________ Lymphocytes are large agranulocytes.