List Koch’s postulates, and explain why they are significant.
Ch. 14 - Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology
All textbooks Bauman 6th Edition
Bauman 6th Edition Ch. 14 - Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology
Ch. 14 - Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology Problem 11.9a
Problem 11.9a
 Bauman 6th Edition
Bauman 6th Edition Ch. 14 - Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology
Ch. 14 - Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology Problem 11.9a
Problem 11.9aChapter 11, Problem 11.9a
Bacteria that convert nitrogen gas into ammonia are __________ .
a. nitrifying bacteria
b. nitrogenous
c. nitrogen fixers
d. nitrification bacteria
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the process of nitrogen fixation, which involves converting nitrogen gas (N2) from the atmosphere into ammonia (NH3).
Identify the role of bacteria in the nitrogen cycle, specifically those that can convert nitrogen gas into ammonia.
Recognize that nitrifying bacteria are involved in converting ammonia into nitrites and nitrates, not in converting nitrogen gas into ammonia.
Consider the term 'nitrogen fixers' and its association with the conversion of nitrogen gas into ammonia.
Evaluate the options given and determine which term correctly describes bacteria that convert nitrogen gas into ammonia.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is the process by which certain bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen gas (N2) into ammonia (NH3), making it available for use by plants. This process is crucial for the nitrogen cycle, as most organisms cannot utilize nitrogen gas directly. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as Rhizobium, often form symbiotic relationships with leguminous plants, enhancing soil fertility.
Recommended video:
Guided course
5 Nitrogenous Bases
Types of Nitrogen-Related Bacteria
There are various types of bacteria involved in the nitrogen cycle, including nitrogen fixers, nitrifying bacteria, and denitrifying bacteria. Nitrogen fixers convert nitrogen gas into ammonia, while nitrifying bacteria oxidize ammonia into nitrites and then nitrates, which plants can absorb. Understanding these distinctions is essential for grasping the roles different bacteria play in soil health and nutrient cycling.
Recommended video:
Guided course

5 Nitrogenous Bases
Role of Ammonia in Agriculture
Ammonia is a key nutrient for plants, serving as a building block for amino acids and proteins. The conversion of nitrogen gas into ammonia by nitrogen-fixing bacteria is vital for agricultural productivity, as it enriches the soil with essential nutrients. This process supports sustainable farming practices by reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers, promoting healthier ecosystems.
Recommended video:
Guided course
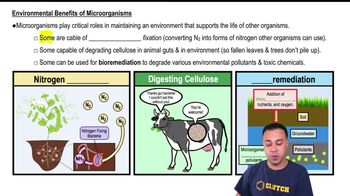
Environmental Benefits of Microorganisms
Related Practice
Textbook Question
157
views
Textbook Question
Given that resistant strains of pathogens are a concern to the general health of a population, what can be done to prevent their development?
25
views
Textbook Question
For each of the following statements that is true, write “true” in the blank. For each statement that is false, write the word(s) that should be substituted for the underlined word(s) to make the statement correct.
__________ Most cyanobacteria form heterocysts in which nitrogen fixation occurs.
29
views
Textbook Question
In which type of symbiosis do both members benefit from their interaction?
a. mutualism
b. parasitism
c. commensalism
d. pathogenesis
36
views
Textbook Question
Endotoxin, also known as ___________, is part of the outer (wall) membrane of Gram-negative bacteria.
38
views
Textbook Question
List four types of symbiotic relationships, and give an example of each.
66
views