Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
DNA and RNA Structure
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids composed of nucleotide sequences. DNA is double-stranded and contains the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In contrast, RNA is typically single-stranded and contains uracil (U) instead of thymine. Understanding the structural differences is crucial for determining how base pairing occurs during transcription.
Recommended video:
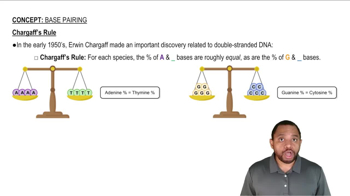
Base Pairing Rules
Base pairing rules dictate how nucleotides pair with each other. In DNA, adenine pairs with thymine (A-T) and cytosine pairs with guanine (C-G). During transcription, the complementary RNA sequence is formed by pairing adenine with uracil (A-U) and cytosine with guanine (C-G). Knowing these rules is essential for accurately determining the mRNA sequence from a given DNA template.
Recommended video:
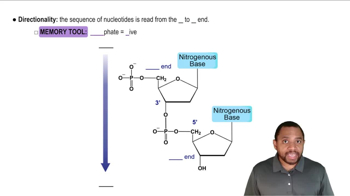
5′ and 3′ Ends
The 5′ and 3′ ends of nucleic acid strands refer to the orientation of the sugar-phosphate backbone. The 5′ end has a phosphate group attached, while the 3′ end has a hydroxyl group. This directional notation is important in molecular biology, as it affects how nucleic acids are synthesized and how they interact during processes like transcription and translation.
Recommended video:
Primary Structure of Nucleic Acids Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance