Textbook Question
If the sequence T-A-C-C-C-T appears on the informational strand of DNA, what sequence appears opposite it on the template strand? Label your answer with 3′ and 5′ ends.
21
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
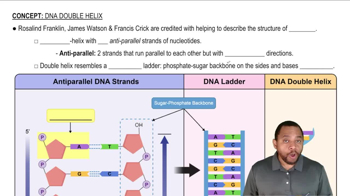

If the sequence T-A-C-C-C-T appears on the informational strand of DNA, what sequence appears opposite it on the template strand? Label your answer with 3′ and 5′ ends.
Look at Table 26.3 and find codons for the following amino acids:
a. Val
Name the nucleoside shown here. Copy the structure, and number the C and N atoms (refer to Table 26.1). <IMAGE>
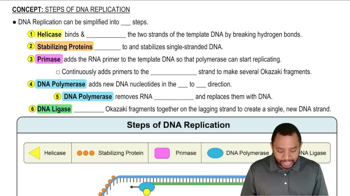
What are Okazaki fragments? What role do they serve in DNA metabolism?
What is the difference between DNA polymerase and DNA ligase?
What is the function of the spliceosome in hnRNA?