Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Heterocyclic Bases
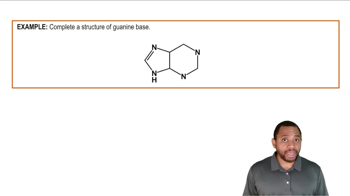
Heterocyclic bases are nitrogen-containing compounds that form the building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. In DNA, these bases are crucial for encoding genetic information and consist of purines and pyrimidines, which are types of heterocycles. Understanding their structure and function is essential for grasping how genetic information is stored and transmitted.
Recommended video:
Nitrogenous Bases Example 3
Purines and Pyrimidines
Purines and pyrimidines are two categories of nitrogenous bases found in DNA. Purines include adenine (A) and guanine (G), while pyrimidines consist of cytosine (C) and thymine (T). The specific pairing of these bases (A with T and C with G) is fundamental to the double-helix structure of DNA and is critical for processes like DNA replication and transcription.
Recommended video:
Nitrogenous Bases Example 1
Base Pairing
Base pairing refers to the specific hydrogen bonding between complementary nitrogenous bases in DNA. This pairing is essential for maintaining the stability of the DNA double helix and ensuring accurate replication and transcription. The rules of base pairing (A-T and C-G) are foundational to molecular biology and genetics, influencing how genetic information is expressed and inherited.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance