Amino Acids
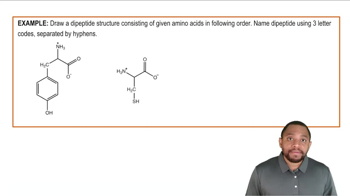
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a distinctive side chain (R group) that determines its properties. Valine, with a nonpolar side chain, is hydrophobic, while serine, with a polar side chain, is hydrophilic, influencing their interactions in proteins.
Recommended video:
Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
Dipeptides
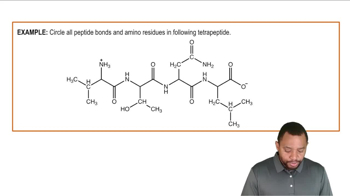
Dipeptides are molecules formed when two amino acids are linked together by a peptide bond. This bond is created through a dehydration synthesis reaction, where a water molecule is released as the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another. The resulting dipeptide retains the characteristics of both amino acids, influencing its overall properties and function.
Recommended video:
Peptide Bond
A peptide bond is a covalent bond that links amino acids together in a protein. It forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another, resulting in the release of a water molecule. This bond is crucial for the structure and function of proteins, as it determines the sequence and arrangement of amino acids in polypeptides.
Recommended video: