Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
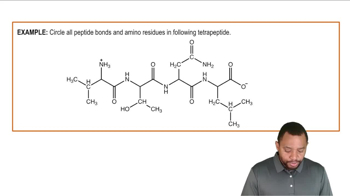
Amino Acids
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, consisting of a central carbon atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain. In the context of vasopressin, which has eight amino acids, each amino acid contributes to the overall structure and function of the protein.
Recommended video:
Amino Acid Catabolism: Amino Group Example 2
Peptide Bonds
Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that link amino acids together in a protein. Formed through a dehydration reaction between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another, each peptide bond reduces the total number of amino acids by one, resulting in a chain of amino acids that constitutes the protein.
Recommended video:
Protein Structure
The structure of a protein is determined by the sequence of amino acids and the interactions between them. In the case of vasopressin, understanding its structure is essential for grasping how many peptide bonds are present, as the number of peptide bonds is always one less than the number of amino acids in the chain.
Recommended video:
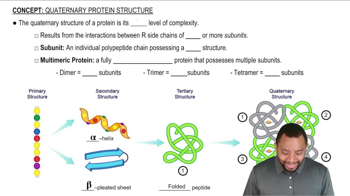
Quaternary Protein Structure Concept 1