Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In organic chemistry, common functional groups include aldehydes and ketones, which contain carbonyl groups (C=O) but differ in their structure. Aldehydes have the carbonyl group at the end of the carbon chain, while ketones have it within the chain.
Recommended video:
Functional Group Priorities Concept 1
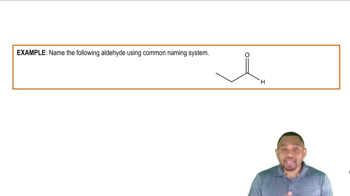
Aldehydes
Aldehydes are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to at least one hydrogen atom. This structure gives aldehydes unique properties, such as their reactivity and ability to participate in various chemical reactions, including oxidation. Common examples include formaldehyde and benzaldehyde, which are used in various industrial and laboratory applications.
Recommended video:
Naming Aldehydes Example 2
Ketones
Ketones are a class of organic compounds characterized by a carbonyl group (C=O) flanked by two carbon atoms. This structure makes ketones distinct from aldehydes, as they do not have a hydrogen atom directly attached to the carbonyl carbon. Ketones are commonly found in solvents and are important in biological processes, with acetone being a well-known example.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance