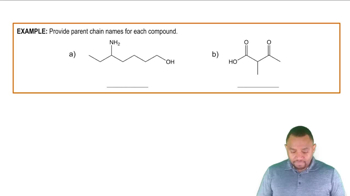
Textbook Question
If one compound has the formula C₅H₁₀ and another has the formula C₄H₁₀ are the two compounds isomers? Explain.
205
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


If one compound has the formula C₅H₁₀ and another has the formula C₄H₁₀ are the two compounds isomers? Explain.
Write condensed structures for the following molecular formulas. More than one isomer will be required for each.
Isomers of C₈H₁₈ that contain two methyl groups and a longest chain of 4 carbons
How many straight-chain isomers can you write that fit the following descriptions? See Worked Example 12.12 for guidance.
Amines (―NH₂) with a longest chain of 7 carbons
Which of the following pairs of structures are identical, which are isomers, and which are unrelated? <IMAGE>
Give IUPAC names for the five isomers with the formula C₆H₁₄.
Draw the structural formulas and name all cyclic isomers with the formula C5H10.