How many straight-chain isomers can you write that fit the following descriptions? See Worked Example 12.12 for guidance.
Amines (―NH₂) with a longest chain of 7 carbons
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


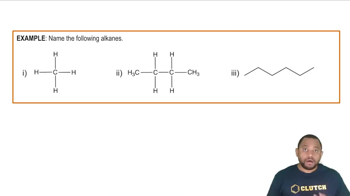
How many straight-chain isomers can you write that fit the following descriptions? See Worked Example 12.12 for guidance.
Amines (―NH₂) with a longest chain of 7 carbons
How many isomers can you write that fit the following descriptions? See Worked Example 12.12 for guidance.
Alcohols (―OH) formed from 2-methylhexane
Which of the following pairs of structures are identical, which are isomers, and which are unrelated? <IMAGE>
Draw the structural formulas and name all cyclic isomers with the formula C5H10.
Draw all possible products formed when 2-methyl-2-butene undergoes addition with HCl. Label them as being either the major or the minor product.
In the following addition reactions, are the given alkyl halides obtained as the major products? Give a reason for your answer.
a. 3-Chloro-3-ethylpentane from addition of HCl to 3-ethyl-2-pentene