Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
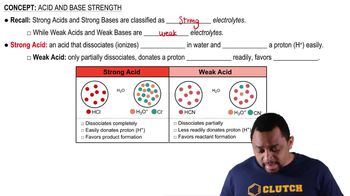
Dissociation of Acids
Dissociation refers to the process by which an acid separates into its constituent ions in solution. For weak acids like trichloroacetic acid, this process is not complete, meaning only a fraction of the acid molecules release protons (H⁺) and form anions. Understanding the degree of dissociation is crucial for calculating the concentrations of ions in solution.
Recommended video:
Acid and Base Strength Concept 1
Concentration Calculations
Concentration is a measure of the amount of a substance in a given volume of solution, typically expressed in moles per liter (M). To find the total concentration of dissolved species, one must account for both the undissociated acid and the ions produced from dissociation. This involves using the initial amount of acid and the percentage that dissociates to determine the final concentrations.
Recommended video:
Percent Concentrations Concept 1
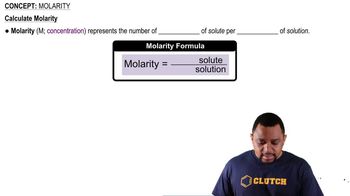
Molarity and Total Ion Concentration
Molarity (M) is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. In this context, to find the total concentration of dissolved ions and molecules, one must consider both the concentration of the dissociated ions and the remaining undissociated acid. The total concentration is the sum of the concentrations of all species present in the solution, providing a comprehensive view of the solution's composition.
Recommended video: