Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. It allows us to calculate the amounts of substances consumed and produced in a reaction based on balanced chemical equations. Understanding stoichiometry is essential for determining how much of one reactant is needed to completely react with another.
Recommended video:
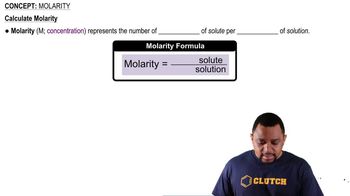
Molarity
Molarity is a measure of concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is expressed in moles per liter (M). In this question, the molarity of BaCl₂ and Na₂SO₄ solutions is crucial for calculating the volume of BaCl₂ needed to react with a given volume of Na₂SO₄, as it directly relates to the number of moles present in the solutions.
Recommended video:
Precipitation Reaction
A precipitation reaction occurs when two soluble salts react in solution to form an insoluble product, known as a precipitate. In this case, the reaction between BaCl₂ and Na₂SO₄ produces BaSO₄, which is insoluble in water. Understanding the nature of precipitation reactions helps in predicting the formation of products and calculating the mass of the precipitate formed.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance