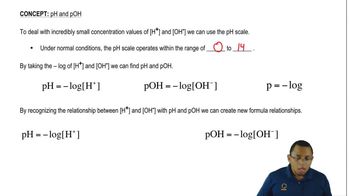Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
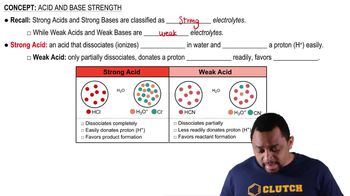
Dissociation of Acids
When a strong acid like HBr is dissolved in water, it completely dissociates into its constituent ions. This means that HBr separates into hydrogen ions (H⁺) and bromide ions (Br⁻), resulting in a solution that has a high concentration of H⁺ ions, which is responsible for the acidic properties of the solution.
Recommended video:
Acid and Base Strength Concept 1
pH Scale
The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14. A pH less than 7 indicates an acidic solution, with lower values representing stronger acids. When HBr is dissolved in water, the increase in H⁺ ions lowers the pH, making the solution highly acidic, often close to 0 for concentrated solutions.
Recommended video:
Ionization in Water
Ionization refers to the process by which molecules break apart into ions in a solvent, such as water. In the case of HBr, the strong acid ionizes completely, meaning that all of the HBr molecules convert into H⁺ and Br⁻ ions. This complete ionization is a characteristic feature of strong acids, distinguishing them from weak acids, which only partially ionize.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance