Textbook Question
Describe the difference between a Lewis structure and a condensed structure in terms of atoms and bonds shown in the structures.
32
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
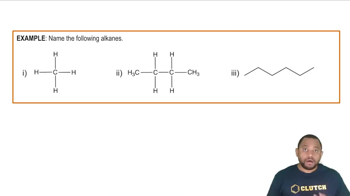


Describe the difference between a Lewis structure and a condensed structure in terms of atoms and bonds shown in the structures.
Explain why it is not possible to draw a skeletal structure for methane.
Use Tables 4.1 and 4.2 to help you answer these practice problems.
Name the straight-chain alkanes or cycloalkanes whose structure or formula is shown:
(b) <IMAGE>
Write the condensed structure for the straight-chain alkanes shown:
(b) methane
Write the condensed structure for the straight-chain alkanes shown:
(c) hexane