Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Anabolism
Anabolism refers to the metabolic processes that build larger molecules from smaller ones, requiring energy input. This includes the synthesis of proteins, nucleic acids, and other macromolecules, which are essential for cell growth and repair. Anabolic reactions are crucial for maintaining and increasing the biomass of organisms.
Recommended video:
Intro to Metabolism Concept 1
Catabolism
Catabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that break down molecules into smaller units, releasing energy in the process. This includes the degradation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to produce ATP, which cells use for energy. Catabolic reactions are vital for providing the energy necessary for various cellular functions.
Recommended video:
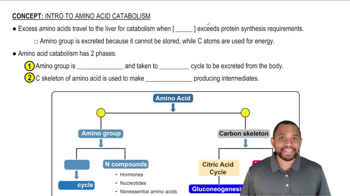
Intro to Amino Acid Catabolism Concept 1
ATP Generation
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) generation is a key process in cellular metabolism, where energy is produced through the breakdown of organic molecules. In the context of catabolism, the breakdown of fructose leads to the production of ATP, which is then used by cells to perform work. Understanding ATP generation is essential for grasping how energy flows within biological systems.
Recommended video:
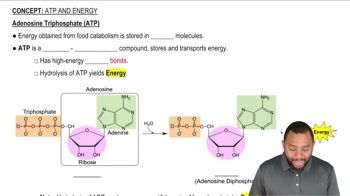
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance