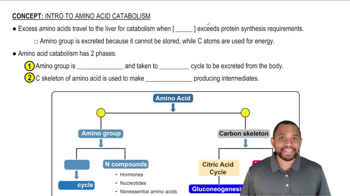
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Catabolic Reactions
Catabolic reactions are metabolic processes that break down larger molecules into smaller units, releasing energy in the process. These reactions are essential for cellular respiration, where glucose is broken down to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell. Understanding the nature of these reactions helps in identifying them based on their energy-releasing characteristics.
Recommended video:
Intro to Amino Acid Catabolism Concept 1
Energy Release
A key feature of catabolic reactions is the release of energy, often measured in calories or joules. This energy is typically harnessed by cells to perform work, such as muscle contraction or biosynthesis. Identifying a reaction as catabolic often involves observing whether it results in a net release of energy, which can be detected through changes in temperature or the production of ATP.
Recommended video:
Biochemical Pathways
Biochemical pathways are sequences of chemical reactions occurring within a cell, where each step is facilitated by enzymes. Catabolic pathways, such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, illustrate how complex molecules are systematically broken down. Recognizing the specific pathways involved can help in identifying catabolic reactions by tracing the transformation of substrates into products.
Recommended video:
Energy Production In Biochemical Pathways Example 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance